Failure and success of the spectral bias prediction
for Laplace Kernel Ridge Regression:
the case of low-dimensional data
@ICML (2022)
Joint work with A. Sclocchi and M. Wyart

The learning algorithm
- Regression of a target function \(f^*\) from \(P\) examples \(\{x_i,f^*(x_i)\}_{i=1,...,P}\).
- Interest in kernels renewed by lazy neural networks
Train loss:
\(K(x,y)=e^{-\frac{|x-y|}{\sigma}}\)
E.g. Laplacian Kernel
- Kernel Ridge Regression (KRR):
- Key object: generalization error \(\varepsilon_t\)
- Typically \(\varepsilon_t\sim P^{-\beta}\), \(P\) number of training data
Predicting generalization of KRR
[Canatar et al., Nature (2021)]
General framework for KRR
- Predicts that KRR has a spectral bias in its learning:
\(\rightarrow\) KRR learns the first \(P\) eigenmodes of \(K\)
\(\rightarrow\) \(f_P\) is self-averaging with respect to sampling
- Obtained by replica theory
- Works well on some real data for \(\lambda>0\)
\(\rightarrow\) what is the validity limit?
Our toy model
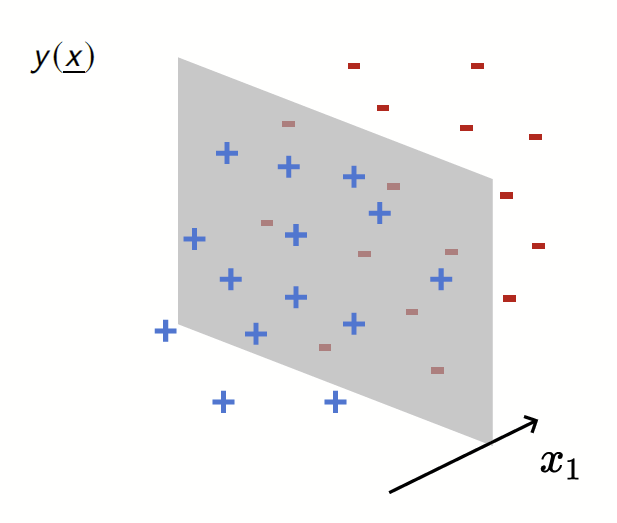
Depletion of points around the interface
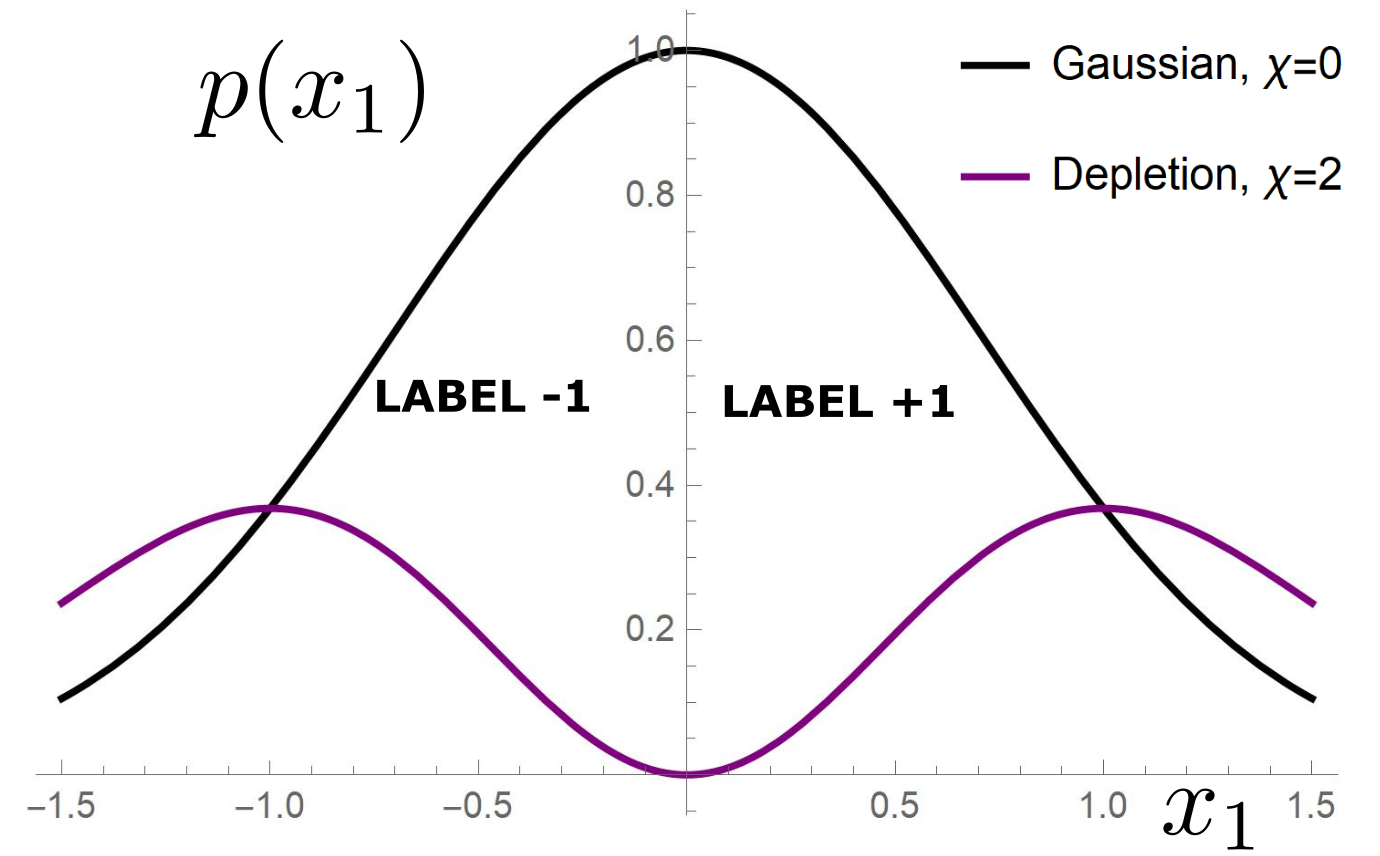
Data: \(x\in\mathbb{R}^d\)
Label: \(f^*(x_1,x_{\bot})=\text{sign}[x_1]\)
Motivation:
evidence for gaps between clusters in datasets like MNIST
Predictor in the toy model
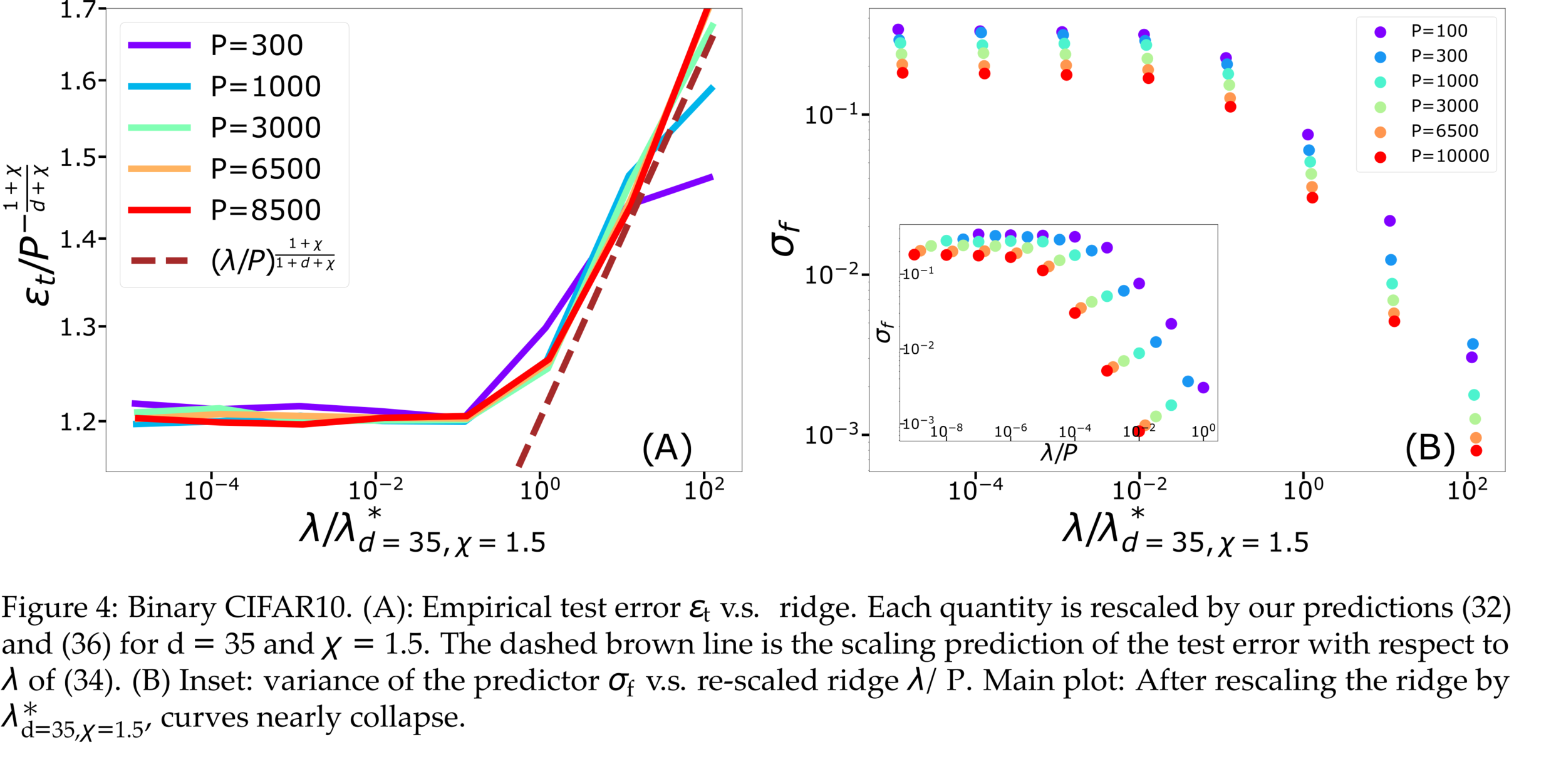
(1) Spectral bias predicts a self-averaging predictor controlled by a characteristic length \( \ell(\lambda,P) \propto \lambda/P \)
For fixed regularizer \(\lambda/P\):
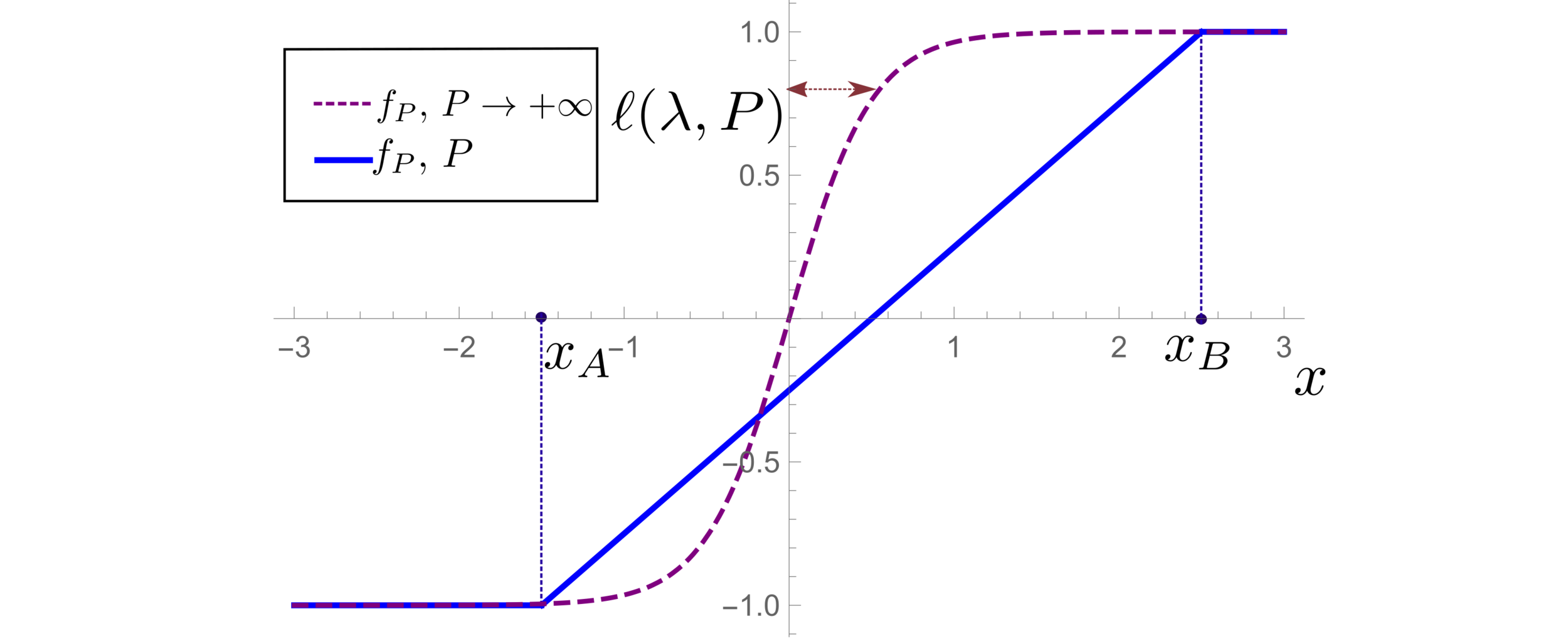
(2) When the number of sampling points \(P\) is not enough to probe \( \ell(\lambda,P) \):
- \(f_P\) is controlled by the statistics of the extremal points \(x_{\{A,B\}}\)
- spectral bias breaks down.
\(d=1\)
Different predictions for
\(\lambda\rightarrow0^+\)
- For \(\chi=0\): equal
- For \(\chi>0\): equal for \(d\rightarrow\infty\)
Crossover at:
\(\lambda\)
Spectral bias failure
Spectral bias success
Conclusions
For small ridge: correct just for \(d\rightarrow\infty\).
Thank you for your attention!
For which kind of data spectral bias fails?
Depletion of points close to decision boundary
Still missing a comprehensive theory for
KRR test error for vanishing regularization
BACKUP SLIDES
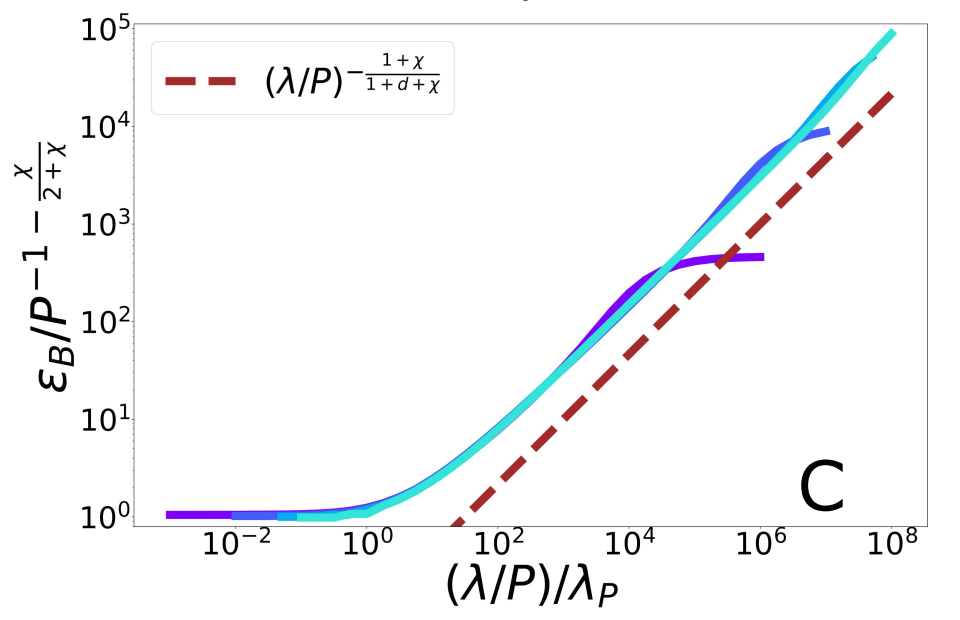
Scaling Spectral Bias prediction
Fitting CIFAR10
Proof:
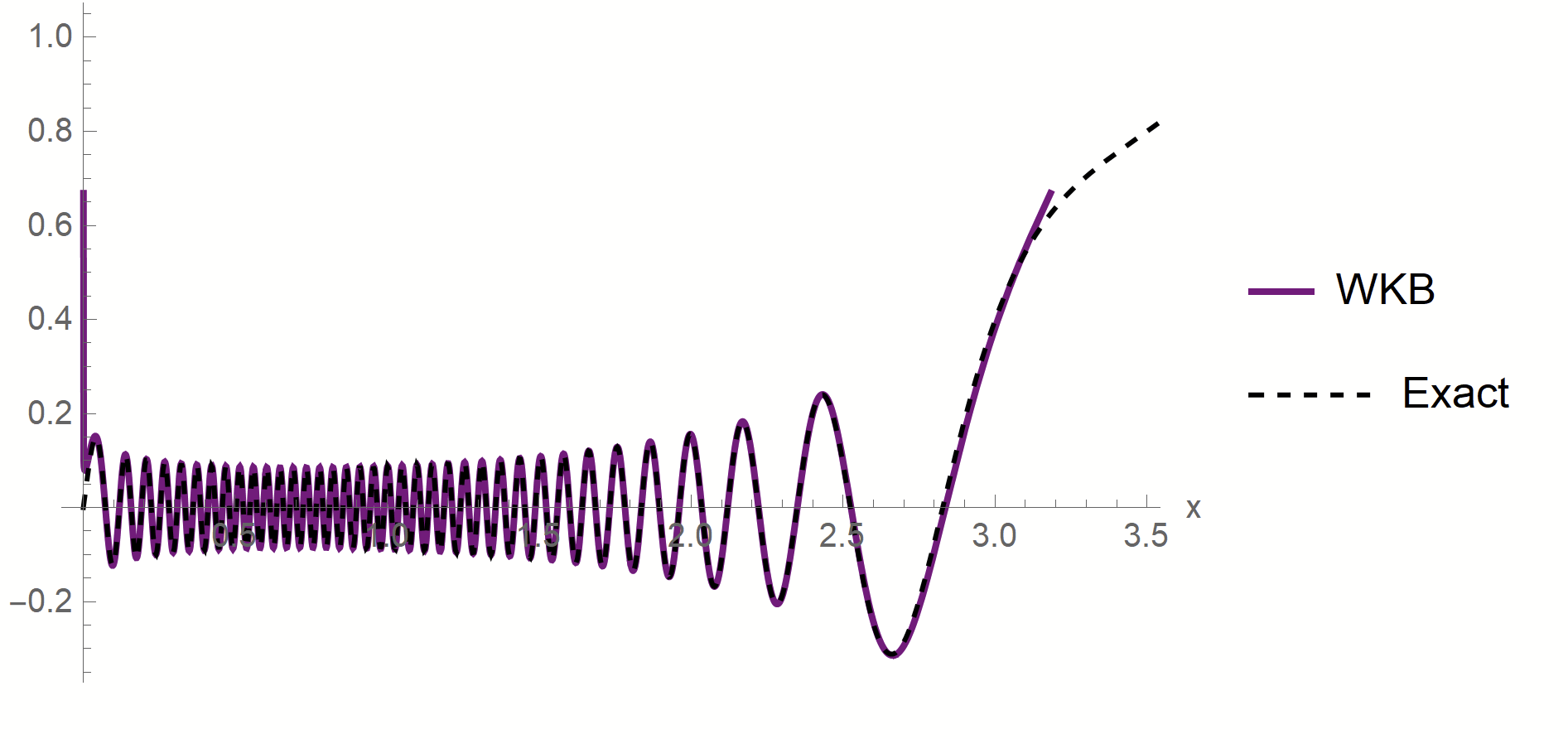
- WKB approximation of \(\phi_\rho\) in [\(x_1^*,\,x_2^*\)]:
\(\phi_\rho(x)\sim \frac{1}{p(x)^{1/4}}\left[\alpha\sin\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{\lambda_\rho}}\int^{x}p^{1/2}(z)dx\right)+\beta \cos\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{\lambda_\rho}}\int^{x}p^{1/2}(z)dx\right)\right]\)
- MAF approximation outside [\(x_1^*,\,x_2^*\)]
\(x_1*\sim \lambda_\rho^{\frac{1}{\chi+2}}\)
\(x_2*\sim (-\log\lambda_\rho)^{1/2}\)
- WKB contribution to \(c_\rho\) is dominant in \(\lambda_\rho\)
- Main source WKB contribution:
first oscillations
Formal proof:
- Take training points \(x_1<...<x_P\)
- Find the predictor in \([x_i,x_{i+1}]\)
- Estimate contribute \(\varepsilon_i\) to \(\varepsilon_t\)
- Sum all the \(\varepsilon_i\)
Characteristic scale of predictor \(f_P\), \(d=1\)
Minimizing the train loss for \(P \rightarrow \infty\):
\(\rightarrow\) A non-homogeneous Schroedinger-like differential equation
\(\rightarrow\) Its solution yields:
Characteristic scale of predictor \(f_P\), \(d>1\)
- Let's consider the predictor \(f_P\) minimizing the train loss for \(P \rightarrow \infty\).
- With the Green function \(G\) satisfying:
- In Fourier space:
- In Fourier space:
- Two regimes:
- \(G_\eta(x)\) has a scale:
FailureSuccess_ICML
By umberto_tomasini
FailureSuccess_ICML
- 9


