Large Scale Identity Data Migration
Issues and Considerations
Why This Matters
- Data migration is often more costly and time-consuming than expected.
- Poor planning leads to project failure.
- Without a proper audit:
- System integrity is not assured.
- Hidden issues may cause data loss or incorrect outcomes.
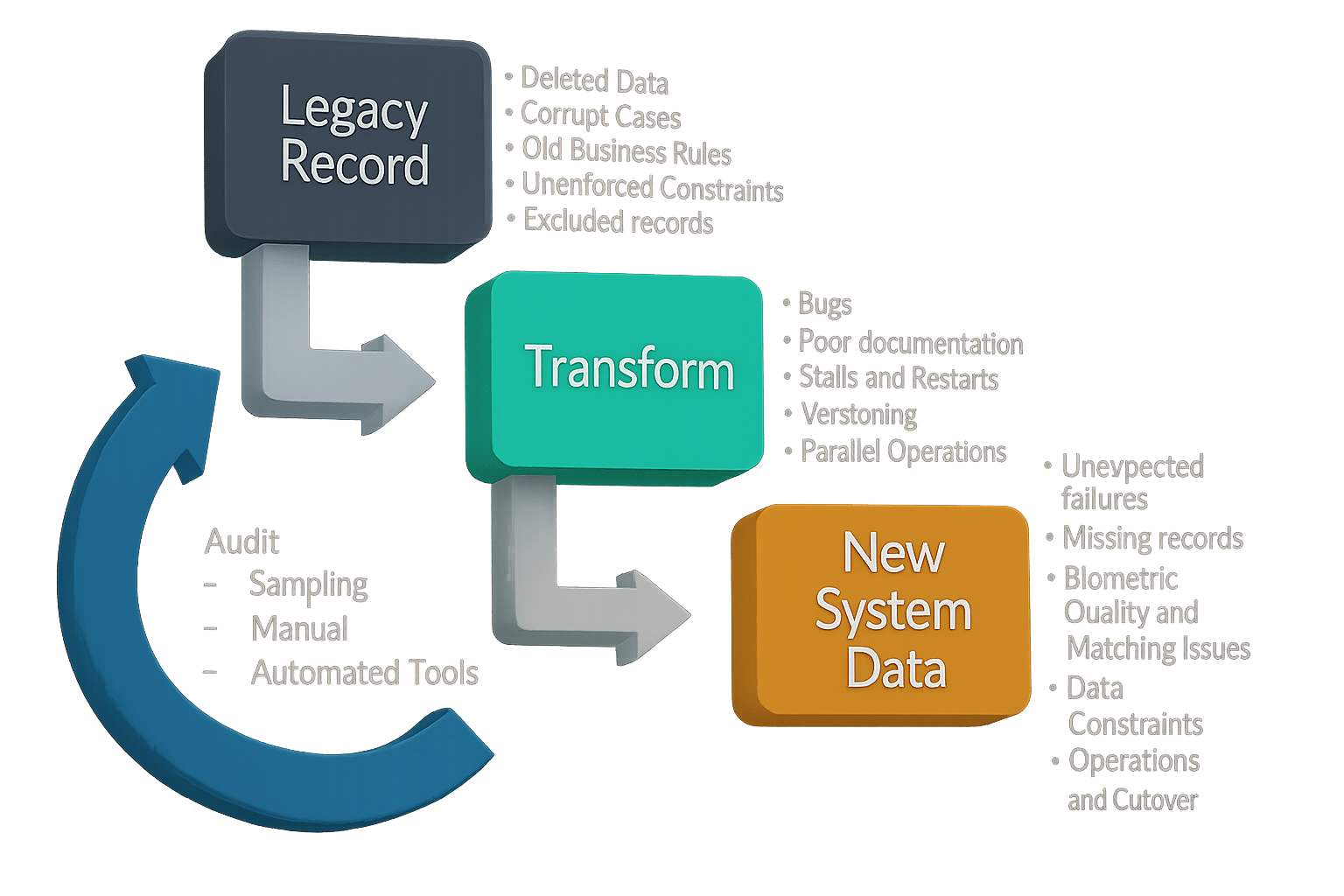
Data Audit Techniques
- Sampling
- Manual review
- Automated tools
Prominent Issues in Data Migration
- New biometric matches
- Data inconsistencies
- Technical implementation errors
- Data reshaping challenges
- Remediation gaps
- Parallel operations difficulties
New Biometric Matches
- New algorithms expose previously undetected issues:
- Matches on previously unlinked individuals
- False positives on prior candidates
- Records with low biometric quality (“untemplate-able”)
Data Inconsistencies
- Example issues from legacy systems:
- Special characters in names
- Inconsistent date formats
- Daylight savings effects
- Legacy business case support
- ...
Technical Implementation Problems
- Unique identifier mix-ups (biometric & biographic)
- Invalid XML/JSON in the database
- Error codes stored in place of actual data
- ...
Data Reshaping Issues
- Adapting old data to a new structure caused:
- Data loss
- Misrepresented relationships
- Loss of visibility of important properties
- ...
Data Remediation Challenges
- Fixes applied without resolving root cause
- Root cause resolved but no remediation applied
- Overlapping issues obscure diagnosis
- No clear “Data Migration Owner”:
- Completion vs. Quality mindset conflict
Parallel Operations Risks
- Hard to keep both systems consistent
- Syncing processes often lag
- Business decisions may be made with outdated data
Conclusion & Recommendations
- Establish Migration team early
- Plan and audit all migration steps
- Use detailed data mapping specs
- Conduct data landscaping upfront
- Biometric Quality important aspect
- Manage outputs across versions
- Prioritize parallel operations support
- Use automated reconciliation tools to ensure:
- Traceability
- Operational assurance
- Targeted remediation
- Confidence in switchover
Copy of Copy of BQAT Gates Presentation
By Ted Dunstone
Copy of Copy of BQAT Gates Presentation
- 7



