Adapting CVSS for Biometric Systems
Addressing Unique Vulnerabilities in Biometric Technologies

Dr Ted Dunstone CEO BixeLab
ted@bixelab.com
Adapting CVSS for Biometric Systems
Addressing Unique Vulnerabilities in Biometric Technologies

Dr Ted Dunstone CEO BixeLab
ted@bixelab.com
Introduction
- Biometric Systems: complex and probabilistic systems. Dependant on acquisition device, quality, environment, demographics
-
Unique Vulnerabilities:
- Spoofing attacks
- Template attacks
- Demographic biases
- Traditional Security Frameworks: Often inadequate in addressing these specific challenges. (mostly deterministic)
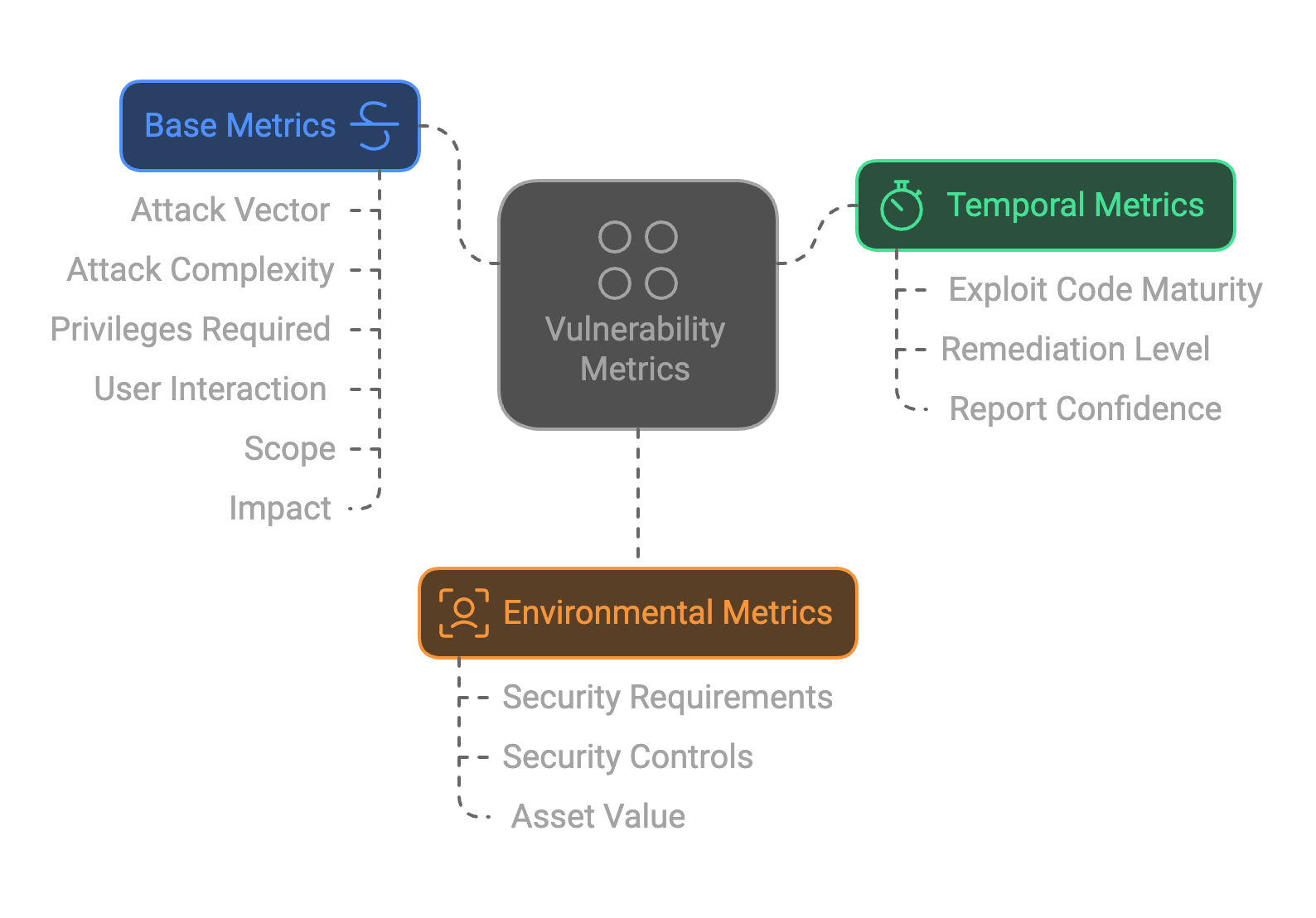
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
- Purpose: Provides a standardized method to assess and communicate the severity of software vulnerabilities.
- Scoring Range: 0 (least severe) to 10 (most severe).
Recent Issues
with CVSS
CVSS impact metrics give equal weight to confidentiality, integrity, and availability, overlooking the unique risk priorities of organizations and the true impact a vulnerability might have,
analysis suggests that around 10% of vulnerabilities are potentially being underrated
JPMorganChase
Has CVSS Been Applied to Biometrics?
- Example: [CVE-2021-3145](https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2021-3145) - Bypass of biometric authentication in Ionic Identity Vault (Android).
- CVSS v3.1 Score: 6.7 (Medium Severity)
This relies on standard metrics that do not fully capture the unique aspects of biometric vulnerabilities, such as spoofing attacks or demographic biases
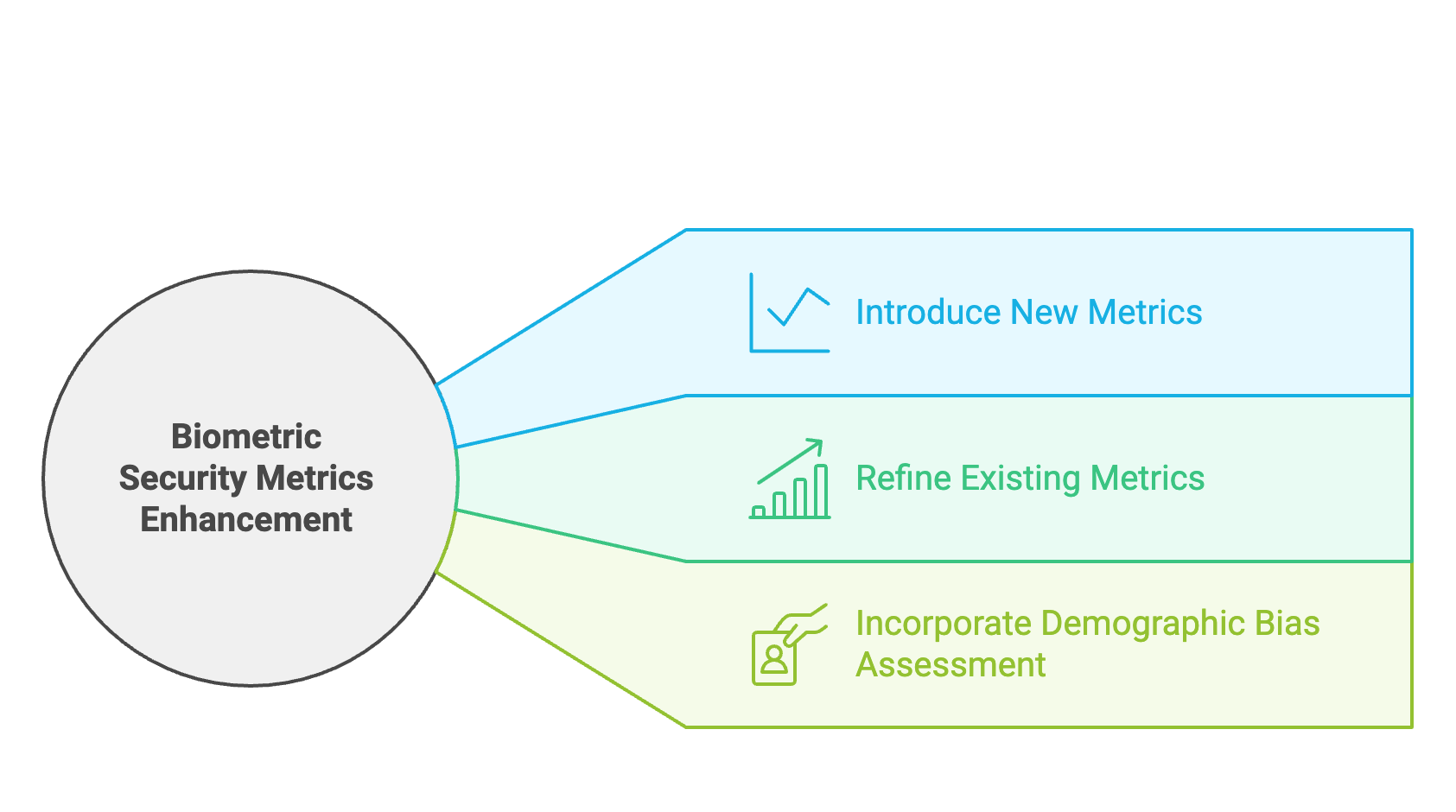
Refine Existing Metric
- Attack Vector: Include physical and digital avenues for biometric data acquisition.
- Impact Metrics: Assess consequences on authentication integrity and privacy breaches.
Incorporate Demographic Bias Assessment
-
Bias Impact: Evaluate vulnerabilities' effects on specific demographic groups, leading to unequal security.
Introduce New Metrics
- Biometric Specificity: Biometric modality issues
- Spoofing Resistance: Measures resistance to spoofing (PAD and Liveness) with Presentation Attack Instruments (PAI) .
Proposal
Recommendations
-
Utilise Biometric-Specific Metrics:
- Template Security: Assess the robustness of stored biometric templates against extraction or reconstruction attacks.
- Liveness Detection Effectiveness: Measure the system's capability to distinguish between live and fake biometric samples.
-
Enhance Environmental Metrics:
- Deployment Context: Consider the operational environment (e.g., controlled access vs. public spaces) to adjust vulnerability severity.
- User Population Diversity: Factor in the diversity of the user base to understand the broader impact of demographic biases.
-
Standardize Reporting of Biometric Vulnerabilities:
- Unified Framework: Encourage the use of adapted CVSS metrics across the industry for consistent vulnerability assessment.
- Regular Updates: Continuously refine metrics to address emerging threats and technological advancements in biometrics.

ICAO Standard Photo Taken

Biometric Data
Store

Biometric Data
Store




Score
0 (not match)
1 (best match)


0.8
Score
0 (not match)
1 (best match)



0.6
Score
0 (not match)
1 (best match)




Score
0 (not match)
1 (best match)




0.5

Score
-100 (not match)
100 (best match)
Score
Frequency
Score
Frequency
Score
Frequency


Score
Frequency


Score
Frequency
Score
Frequency


Score
Frequency


Score
Frequency
Threshold
Score
Frequency
Threshold
Score
Frequency
Threshold
❌


Score
Frequency

✅
❌



Threshold

stored
reference



stored
reference
probe
reference
✅


stored
reference
probe
reference
comparison
Threshold

stored
reference
probe
reference
comparison
Threshold
❌


stored
reference
probe
reference
comparison



stored
reference
probe
reference
comparison

stored
reference


stored
reference
probe
reference
comparison

stored
reference
comparison


stored
reference
probe
reference
comparison

stored
reference
comparison




stored
reference
probe
reference
comparison

stored
reference
comparison



✅
❌
Raw Biometric
Template
Quality
Transaction
Biographics

Raw Biometric
Template
Quality
Transaction
Biographics
Examples
Example 1: Spoofing Attack on Facial Recognition System
- Scenario: An attacker uses a high-resolution photograph to spoof a facial recognition system.
-
Assessment Using Adapted CVSS:
- Attack Vector (AV): Physical
- Attack Complexity (AC): Low
- Privileges Required (PR): None
- User Interaction (UI): Required
- Spoofing Resistance (SR): Low
- Impact on Authentication Integrity (IAI): High
- Bias Impact (BI): Medium
- Resulting Score: 8.0 (High)
Face Recognition Example
1. Attack Vector (AV): Physical (P)
- The attacker must physically present a high-resolution photograph to the facial recognition system to execute the spoofing attack.
2. Attack Complexity (AC): Low (L)
- The attack does not require special conditions or advanced skills; a readily available photograph suffices.
3. Privileges Required (PR): None (N)
- The attacker does not need any prior access or privileges within the system to perform the attack.
4. User Interaction (UI): Required (R)
- The attack necessitates interaction with the system, such as presenting the photograph to the camera.
5. Scope (S): Unchanged (U)
- The attack impacts the vulnerable component (facial recognition system) without affecting other system components.
6. Confidentiality Impact (C): None (N)
- The attack does not directly compromise confidential information.
7. Integrity Impact (I): High (H)
- The attack allows unauthorized access, compromising the integrity of the authentication process.
8. Availability Impact (A): None (N)
- The attack does not affect the availability of the system.
Integrating Adapted CVSS into Security Strategies
-
Risk Assessment:
- Use CVSS scores to prioritize remediation efforts
-
System Design:
- Include spoofing resistance and strong template security in development.
-
Policy Development:
- Set guidelines for regular biometric system assessments
-
Training and Awareness:
- Inform stakeholders about biometric vulnerabilities and the need for tailored security assessments.
Conclusion
- Necessity: Biometric system are increasing used in both Foundation and Function Identity (e.g. Passkeys).
-
Benefits of Adapted CVSS (BCVSS?):
- Standardizes the assessment of biometric vulnerabilities.
- Strengthens authentication and identification technologies.
- Call to Action: Contact ted@bixelab.com to collaborate
References
BixeLab BQAT v2.0
Commercial-in-Confidence, © 2024 BixeLab Pty Ltd
Introduction to BQAT
The Biometric Quality Assessment Tool (BQAT) is an open-source quality assessment tool for analyzing and generating biometric sample quality to international standards.
Supported biometric modalities include:
- Fingerprint
- Face
- Iris
- Voice

ID: 1232324



Output Results
- Results are provided in CSV format.
EDA Report
- Includes exploratory data analysis (EDA) of biometric sample quality.
Quality Metrics (Face)
Customised Attributes:
- Position: Image is vertically and horizontally centered.
- Composition: Minimum 50% of the image must contain the face.
- Eye: Eyes must be open, visible, looking straight into the camera, and free of red-eye.
- Expression: Neutral or slight smile (with lips closed).
- Head Orientation: Variability is no more than 5% in any three directions.
- Shadow: No shadows on the image.
- Background: Plain white, light grey, or light blue background with no objects.
- Image Brightness: The image should not be too bright or too dark.
- Hair: Hair must not cover the face.
- Headgear: Only dark-colored religious headgear that does not cover the face is acceptable.
Deployment
- All BQAT variants are packaged as Docker images and ready to be deployed as Docker containers.
Prerequisites:
- Windows / Linux (preferred)
- Docker engine installed
Installation:
- Refer to the manual to download Docker containers and run BQAT.
Potential Technical Errors
- "Server not found": Verify the URL.
- Frozen tasks: If the BQAT task is taking too long, large datasets may require more processing time. If significantly delayed, cancel and restart the task.
Outlier Detection (Beta)
- Beta feature for identifying outliers based on metrics.
- Multiple outlier detection algorithms available.
- Consistent algorithm usage is recommended.
Example:
- Metric: "Head size"
- Bigger than others
- Smaller than others
Contact Information
- Address: 3/16 Bentham Street, Yarralumla ACT 2600
- Dr. Ted Dunstone – Senior Responsible Officer: ted@bixelab.com
- Mr. Liam Wu – Senior Engineering Lead: Liam.wu@biometix.com
- Ms. Somya Singh – Operations Manager: s.singh@bixelab.com
Commercial-in-Confidence, © 2024 BixeLab Pty Ltd
Copy of Adapting CVSS for Biometric Systems
By Ted Dunstone
Copy of Adapting CVSS for Biometric Systems
- 122



