ZPAN
Subproblem 1
Prediction of first Acute Pancreatitis Diagnosis
Subproblem 1 - First A.P. diagnosis prediction
Inclusion Criteria:
35-65 years old patients with >= 2 years of records available
Exclusion Criteria:
Patients with any Drug- or Alcohol-Induced Acute Pancreatitis (K85.2, K85.3) are excluded.
Prediction Target: Acute Pancreatitis (except for drug- and alcohol-induced A.P. (K85, K85.0, K85.1, K85.8, K85.9)
Time of Prediction: Case: 6 to 18 months before first target Dx; Control: 2 years before end of records
Observation window: 1 to 2 years leading to the time of prediction
Prediction Objective: Predict if any Target diagnosis will be recorded within 6 to 18 months following the time of prediction
Cohort Size:
Case: 46,135 (0.8%), Control: 5,586,388 (99.2%)
Males: 2,513,756 (44.6%), Females: 3,118,767 (55.4%)
Mean age at the time of prediction: 50 years 4 months
Patients with Other diseases of pancreas (K86) at the time of first K85 diagnosis:
Case: 1,230 (2.7%), Control: 9,231 (0.2%)
Subproblem 1 - First A.P. diagnosis prediction
General Performance
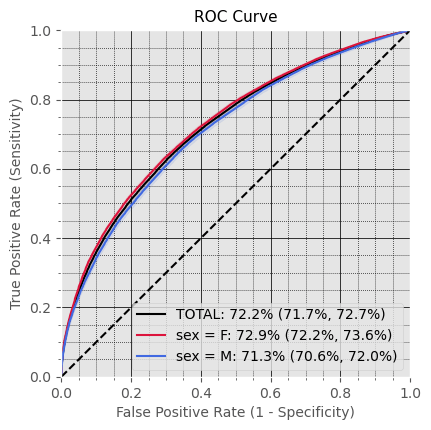
Subproblem 1 - First A.P. diagnosis prediction
Most influential Diagnostic Codes by mean absolute SHAP value across all True Positive patients
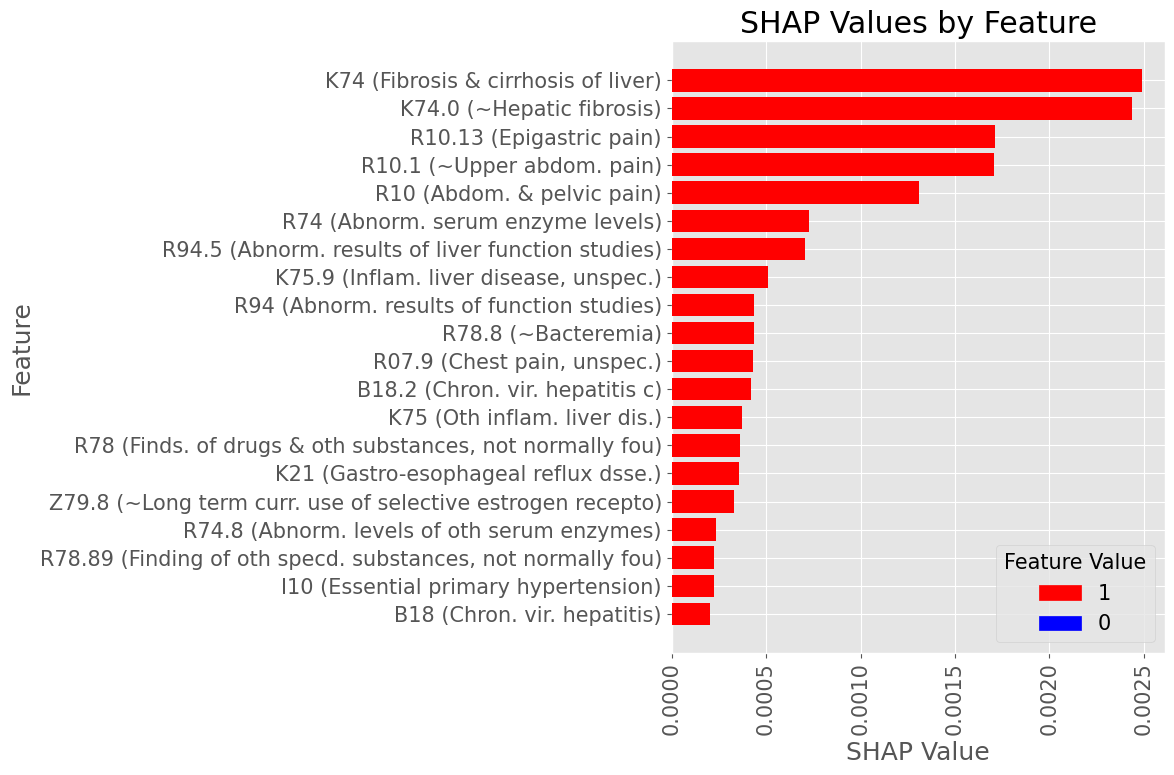
Male Subset
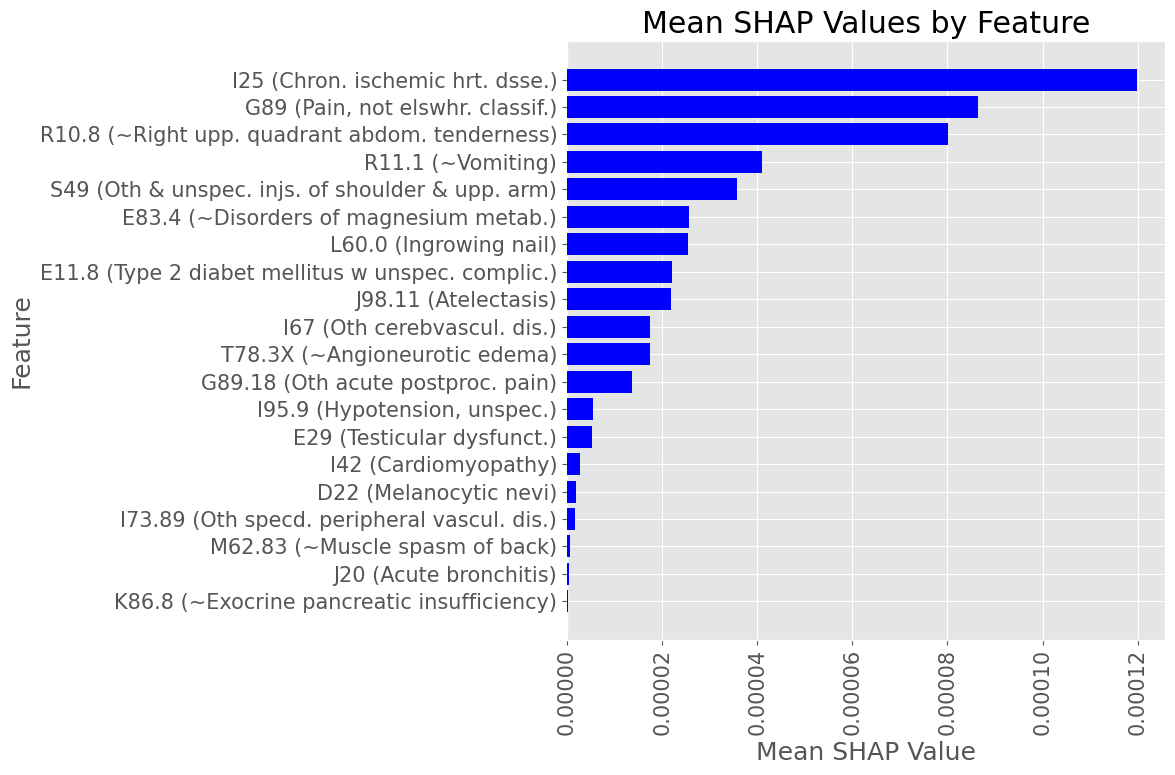
Subproblem 1 - First A.P. diagnosis prediction
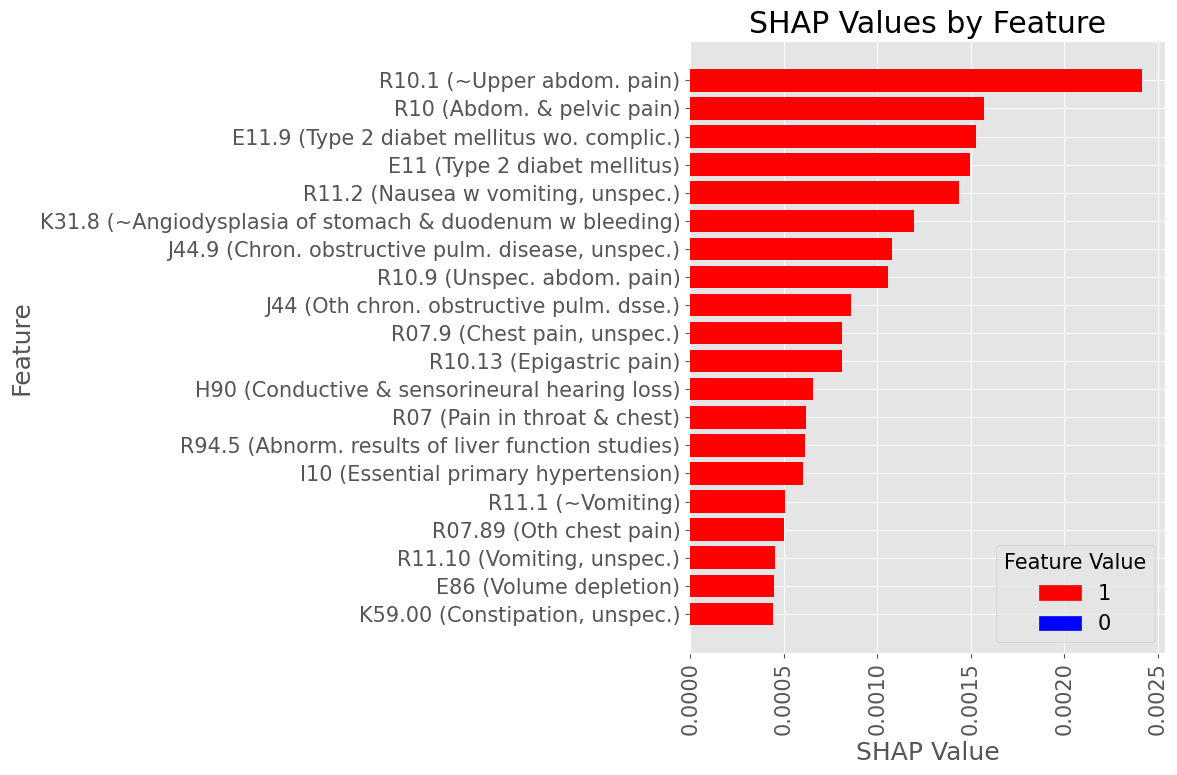
Most influential Diagnostic Codes by mean absolute SHAP value across all True Positive patients
Female Subset
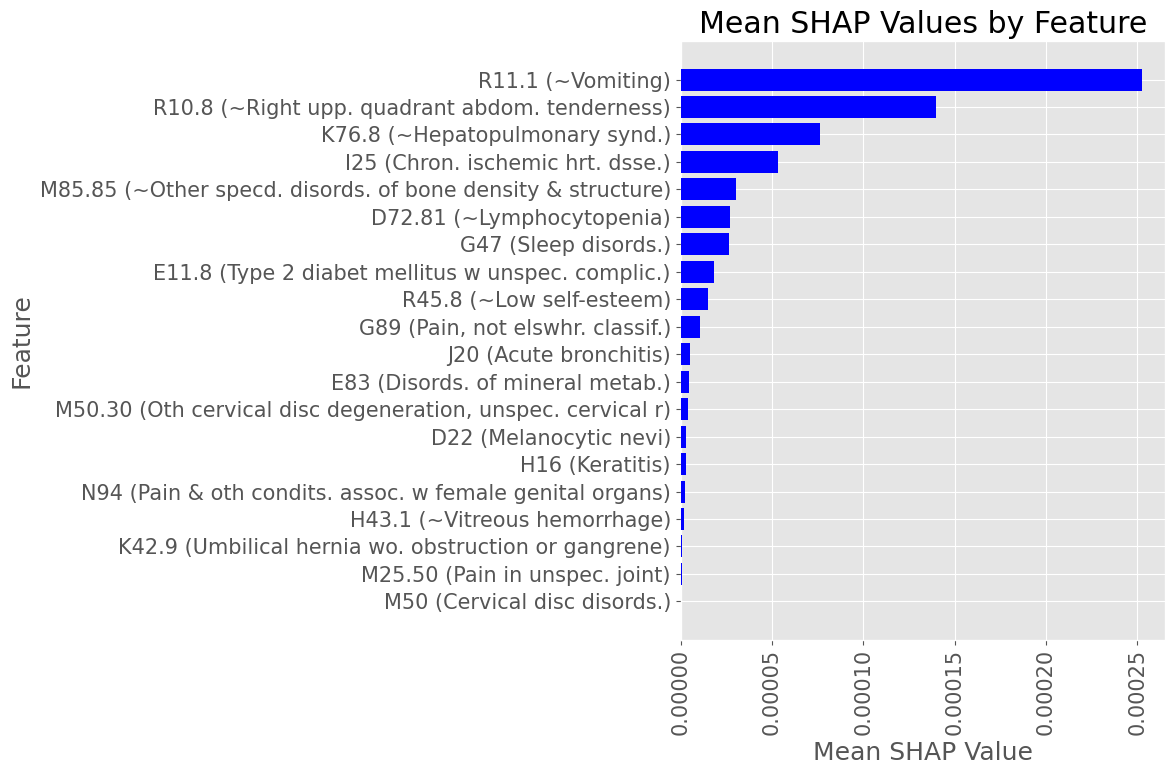
Subproblem 1 - First A.P. diagnosis prediction
Examples of most influential codes for True Positive patients
Male Subset
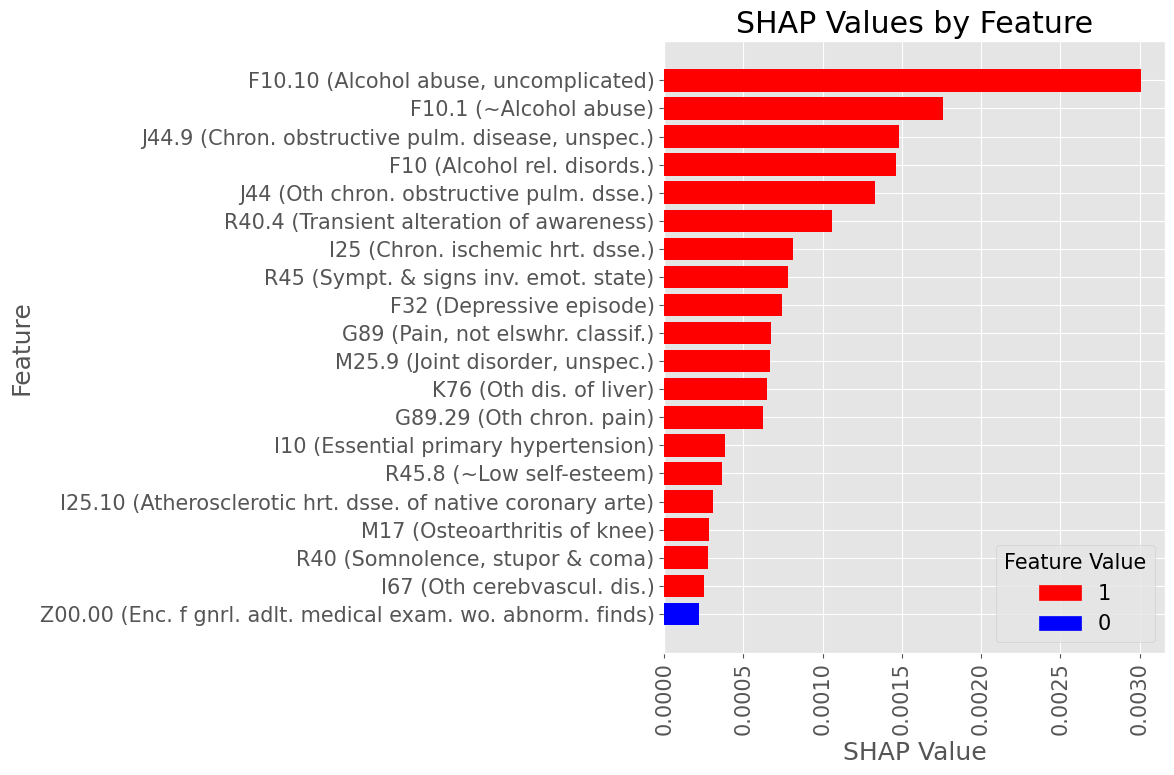
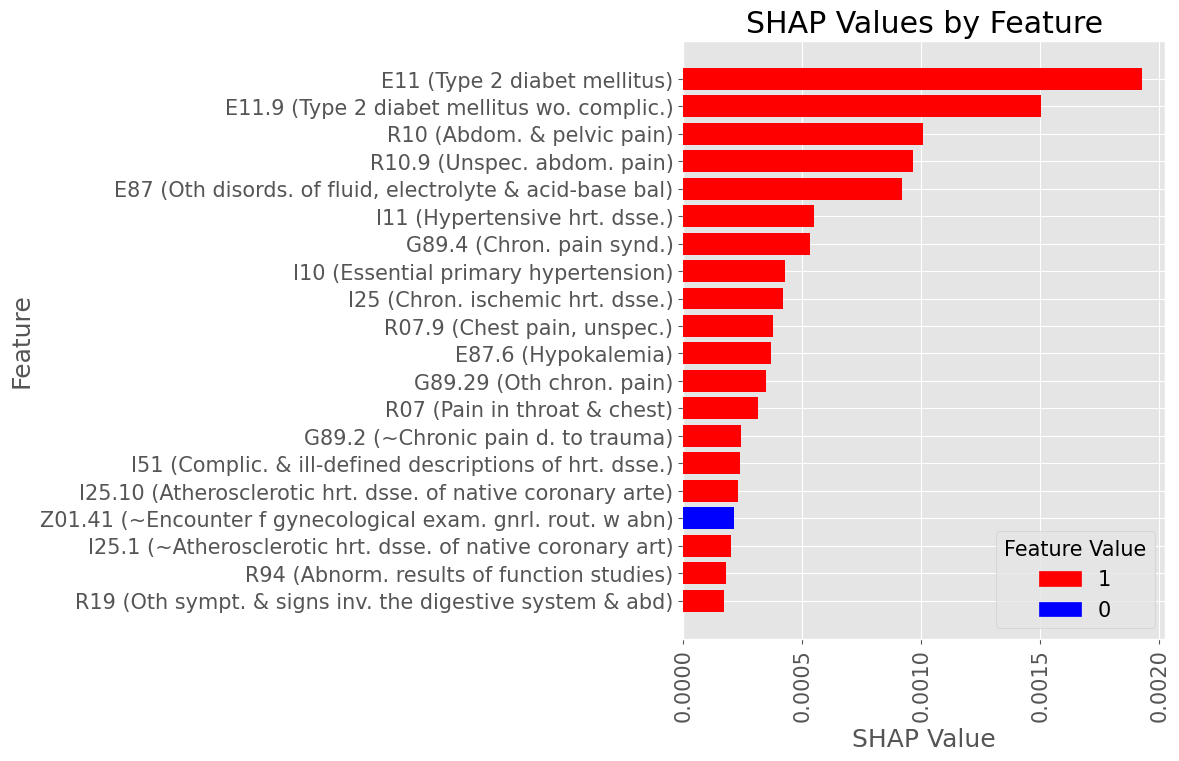
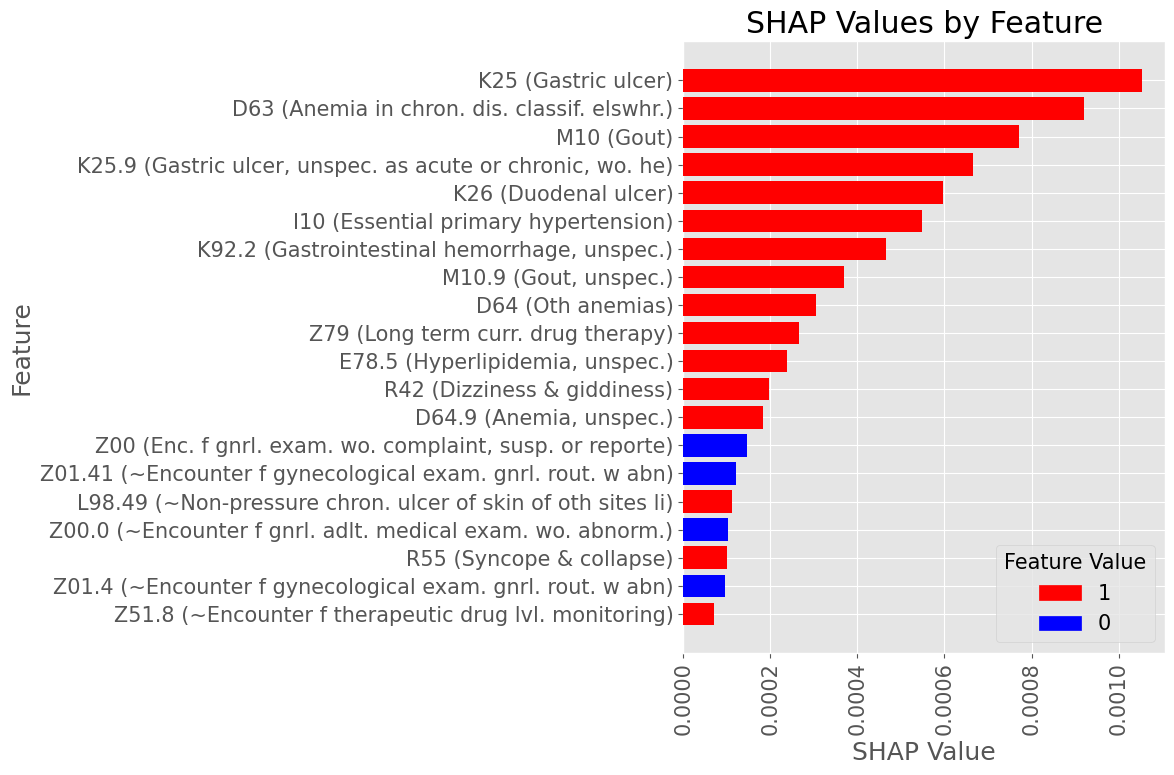
Subproblem 1 - First A.P. diagnosis prediction
Examples of most influential codes for True Positive patients
Female Subset
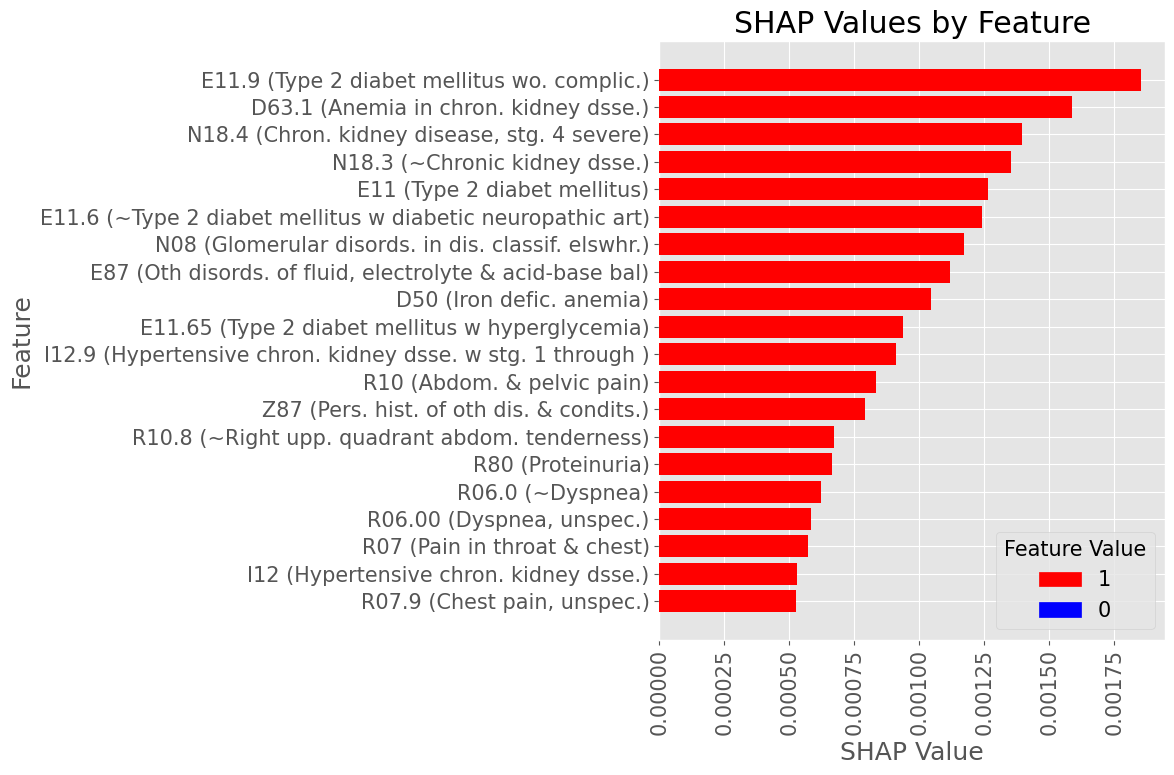
Subproblem 1
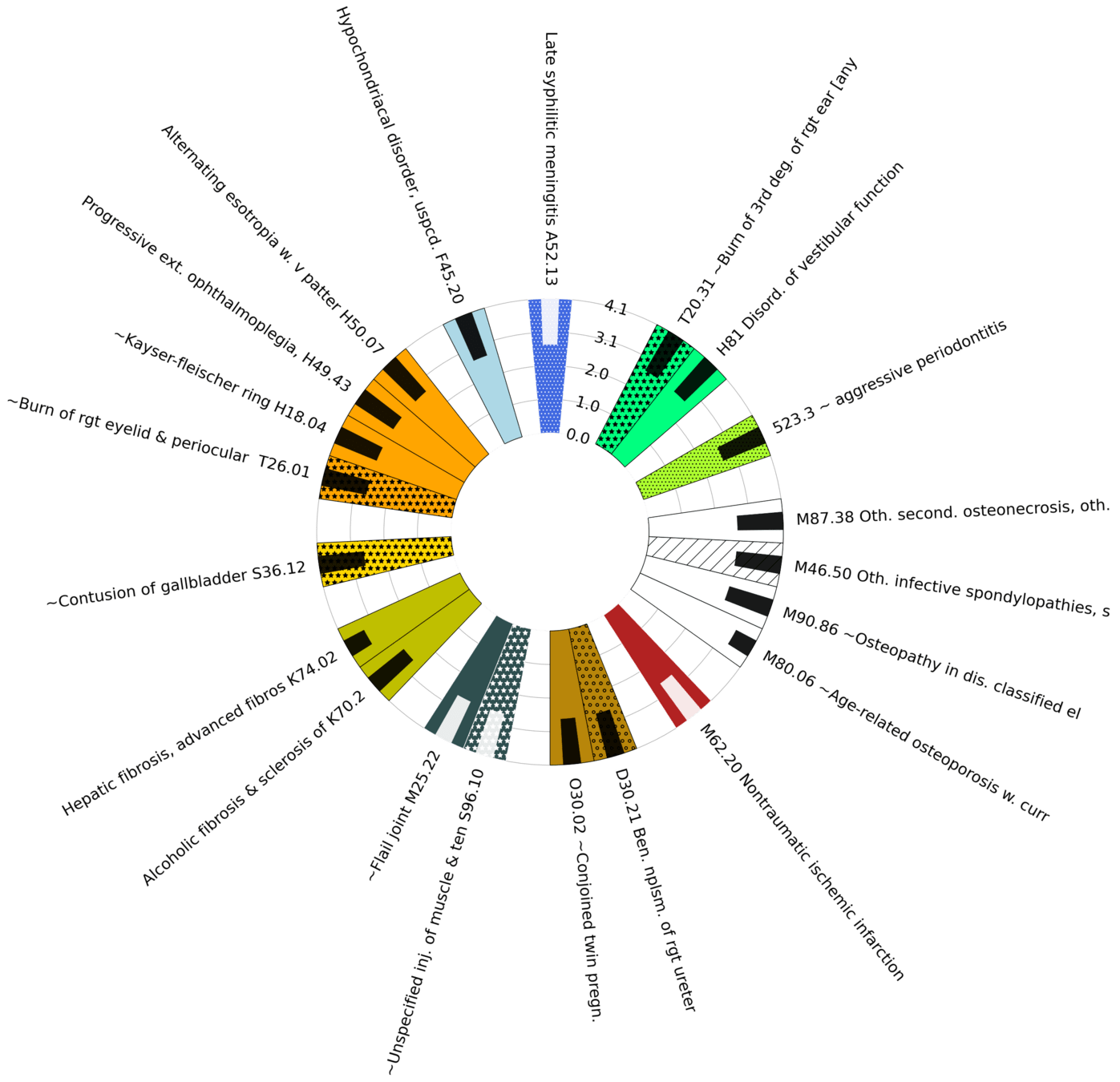
Diagnoses with Highest statistically significant Log Odds Ratios by organ group

Subproblem 1
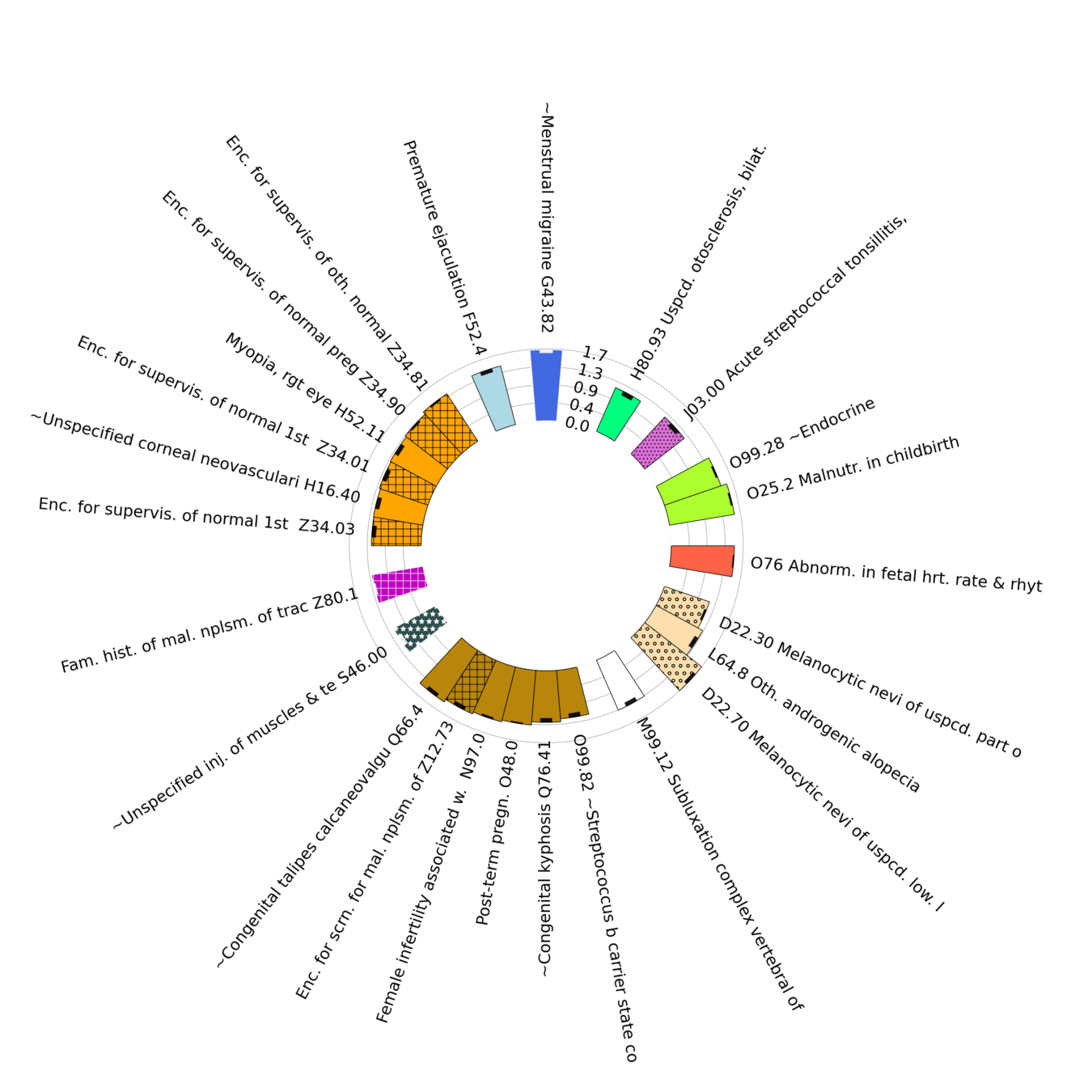
Diagnoses with Lowest statistically significant Absolute Log Odds Ratios by organ group

Questions:
- Is current prediction window (6 to 18 month following screening) useful for the stated purpose? Should it be shorter or longer?
- Are any of the top-risk codes presented in the slides above solid proxies for A.P. diagnosis? If so, should such codes be included into the prediction target, or filtered out from the cohort?
ZPAN
Subproblem 2.1
Progression from A.P. to Diabetes Mellitus due to underlying conditions
Subproblem 2.1 - Progression from A.P. to Diabetes Mellitus due to underlying conditions
Inclusion Criteria:
Patients of any age with any K85 (Acute Pancreatitis) code recorded, with >= 1 year of records leading to the first K85 diagnosis available
Exclusion Criteria:
Patients with any Diabetes Mellitus prior to the first K85 diagnosis are excluded.
Prediction Target: Diabetes Mellitus due to Underlying Conditions (E08, E13)
Time of Prediction: Date of the first K85 diagnosis
Observation window: 1 to 2 years leading to the first K85 diagnosis
Prediction Objective: Predict if any Target diagnosis will be recorded within 2 weeks to 2 years following the first K85 diagnosis
Cohort Size:
Case: 1,329 (1.1%), Control: 122,257 (98.9%)
Males: 52,427 (42.4%), Females: 71,159 (57.6%)
Mean age at the time of prediction: 51 years 5 months
Patients with Other diseases of pancreas (K86) at the time of first K85 diagnosis:
Case: 397 (29.9%), Control: 17,051 (13.9%)
Subproblem 2.1 - Progression from A.P. to Diabetes Mellitus due to underlying conditions
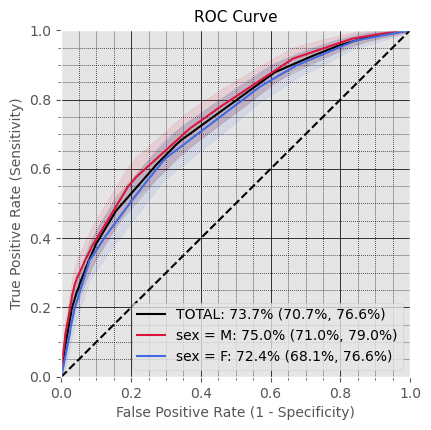
General Performance
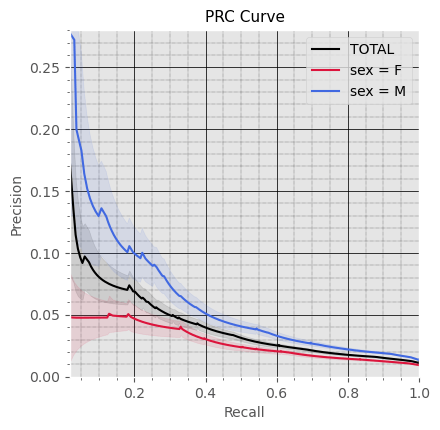
Subproblem 2.1 - Progression from A.P. to Diabetes Mellitus due to underlying conditions
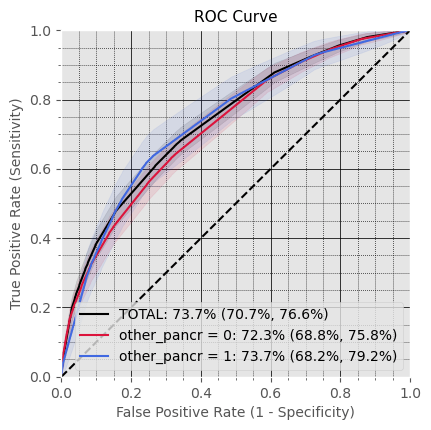
Performance for subsets with and without Other diseases of Pancreas (K86)
in Observation Window
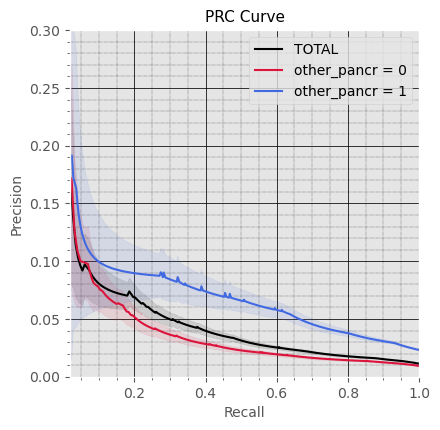
Subproblem 2.1 - Progression from A.P. to Diabetes Mellitus due to underlying conditions
Most influential Diagnostic Codes by mean absolute SHAP value across all True Positive patients
Male Subset
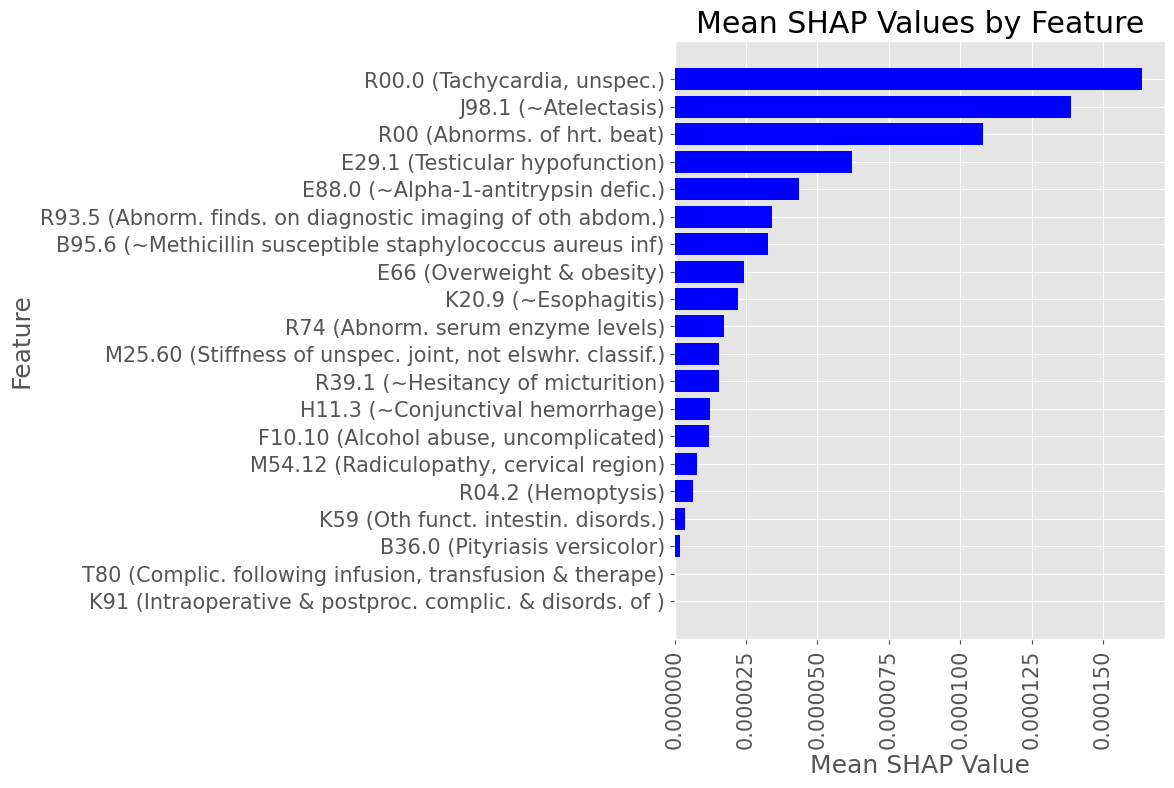
Subproblem 2.1 - Progression from A.P. to Diabetes Mellitus due to underlying conditions
Most influential Diagnostic Codes by mean absolute SHAP value across all True Positive patients
Female Subset
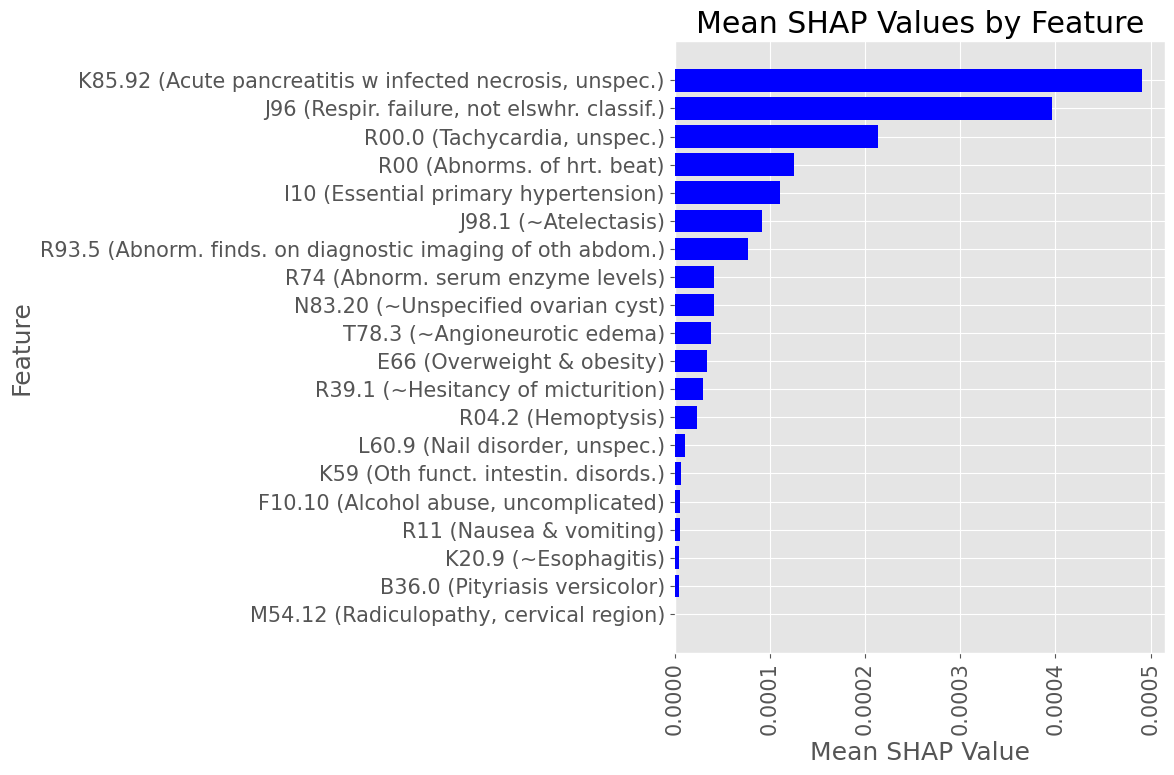
Subproblem 2.1 - Progression from A.P. to Diabetes Mellitus due to underlying conditions
Examples of most influential codes for True Positive patients
Male Subset
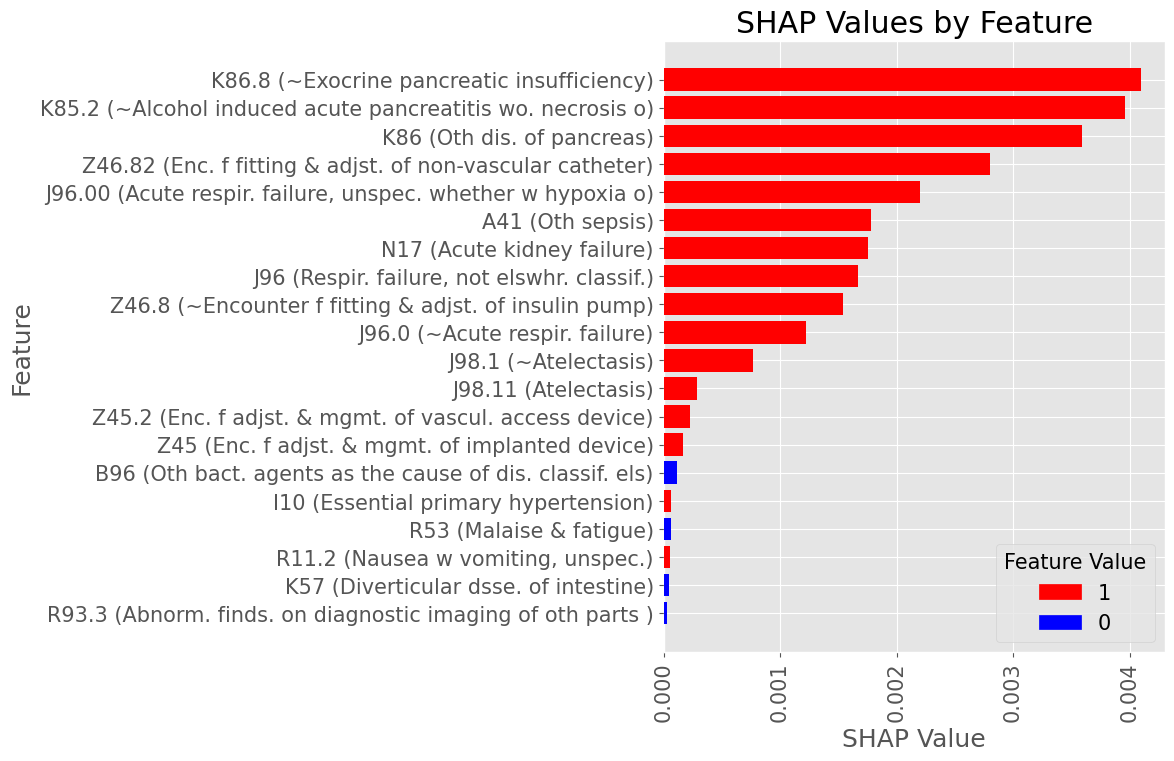
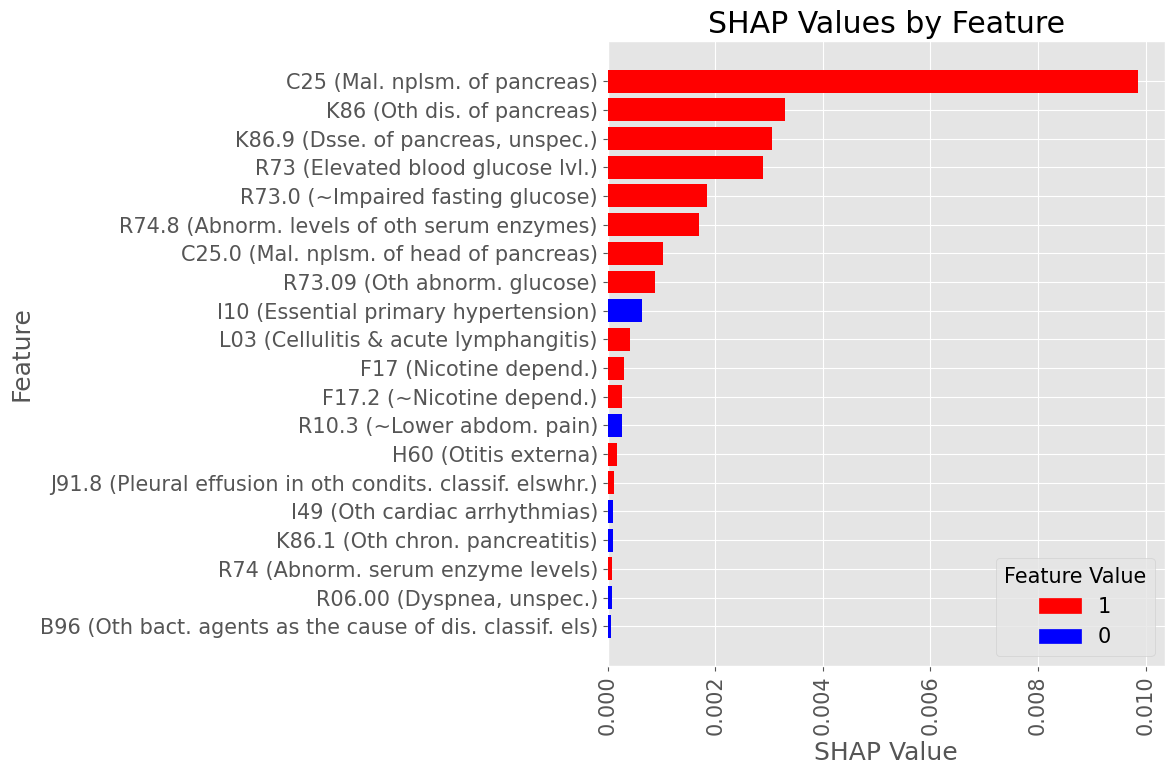
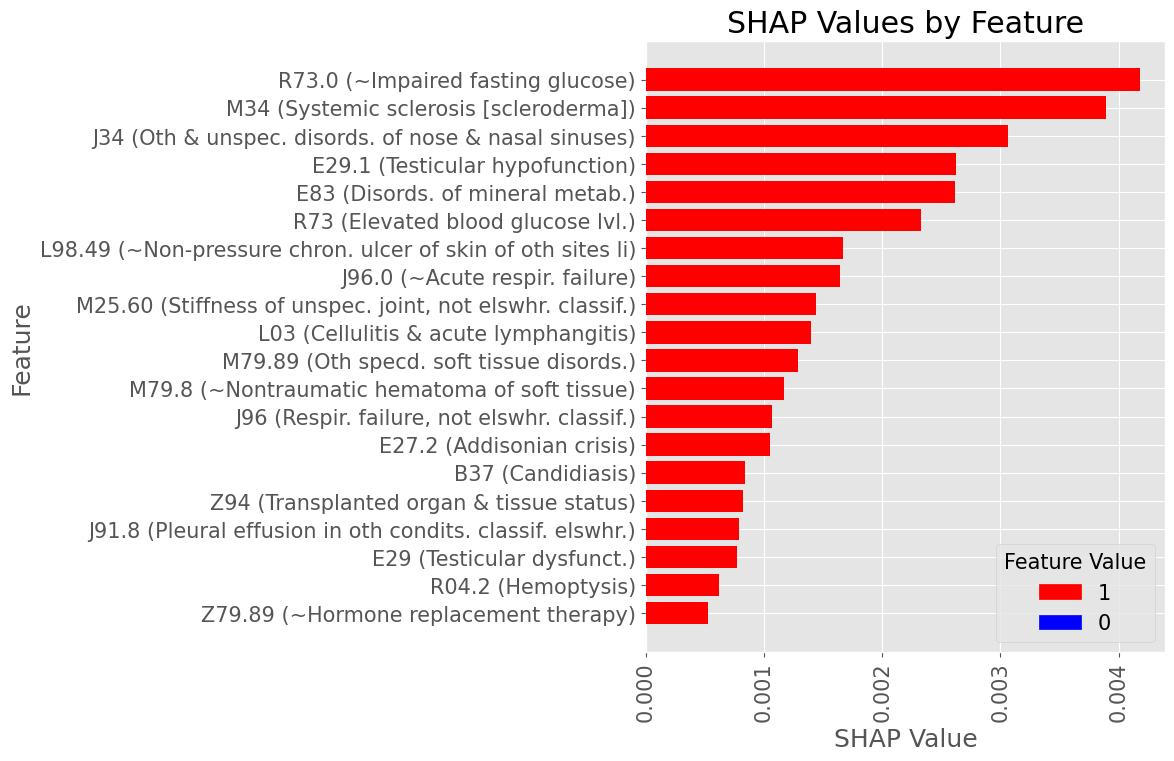
Subproblem 2.1 - Progression from A.P. to Diabetes Mellitus due to underlying conditions
Examples of most influential codes for True Positive patients
Female Subset
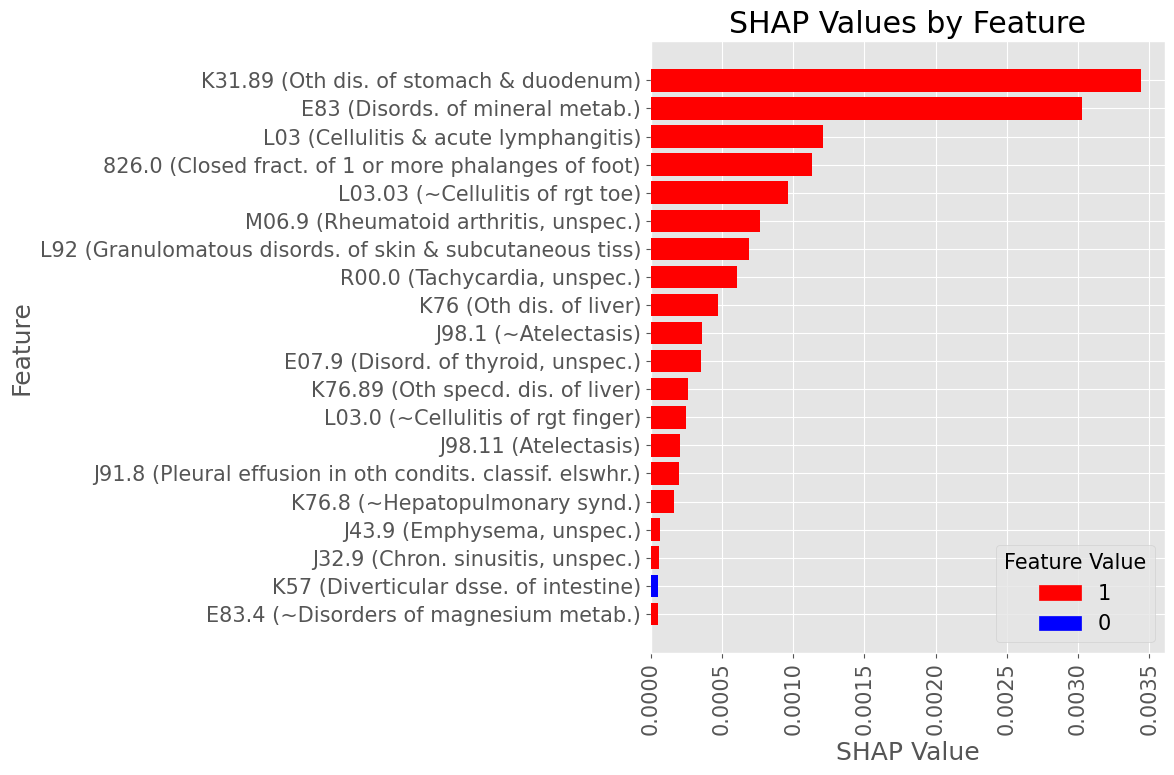
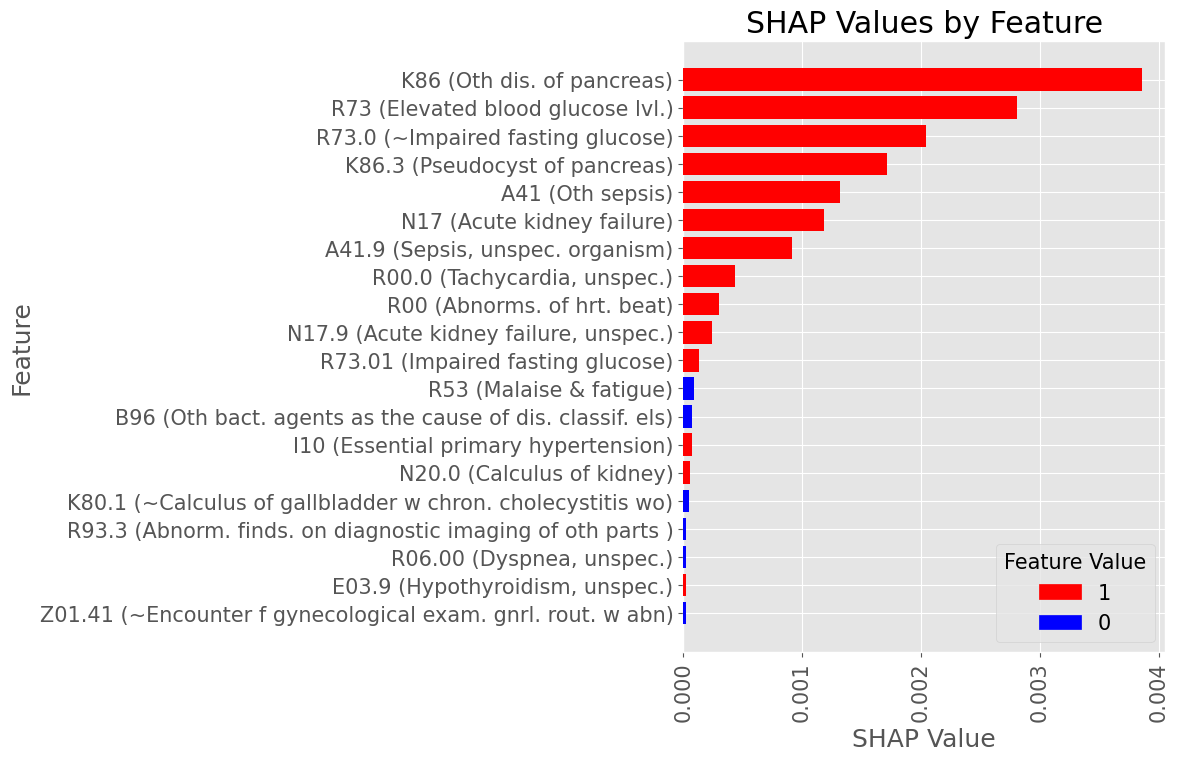
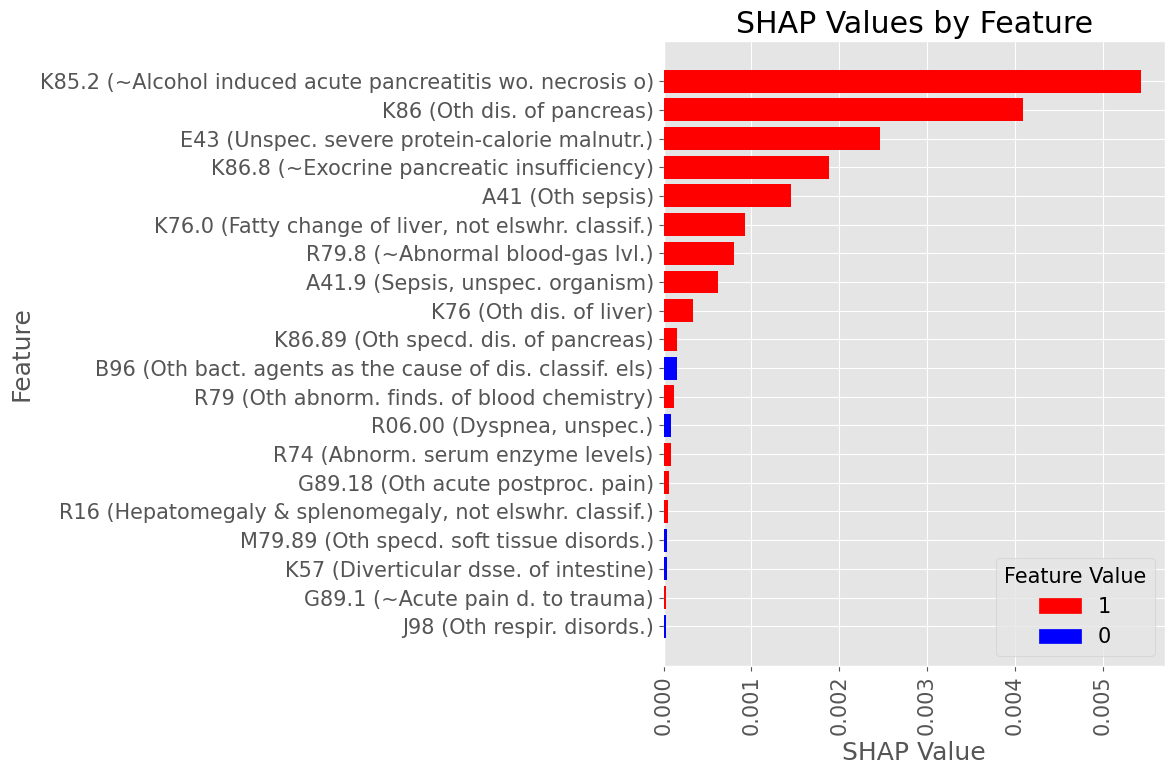
Subproblem 2.1
Diagnoses with Highest statistically significant Log Odds Ratios by organ group
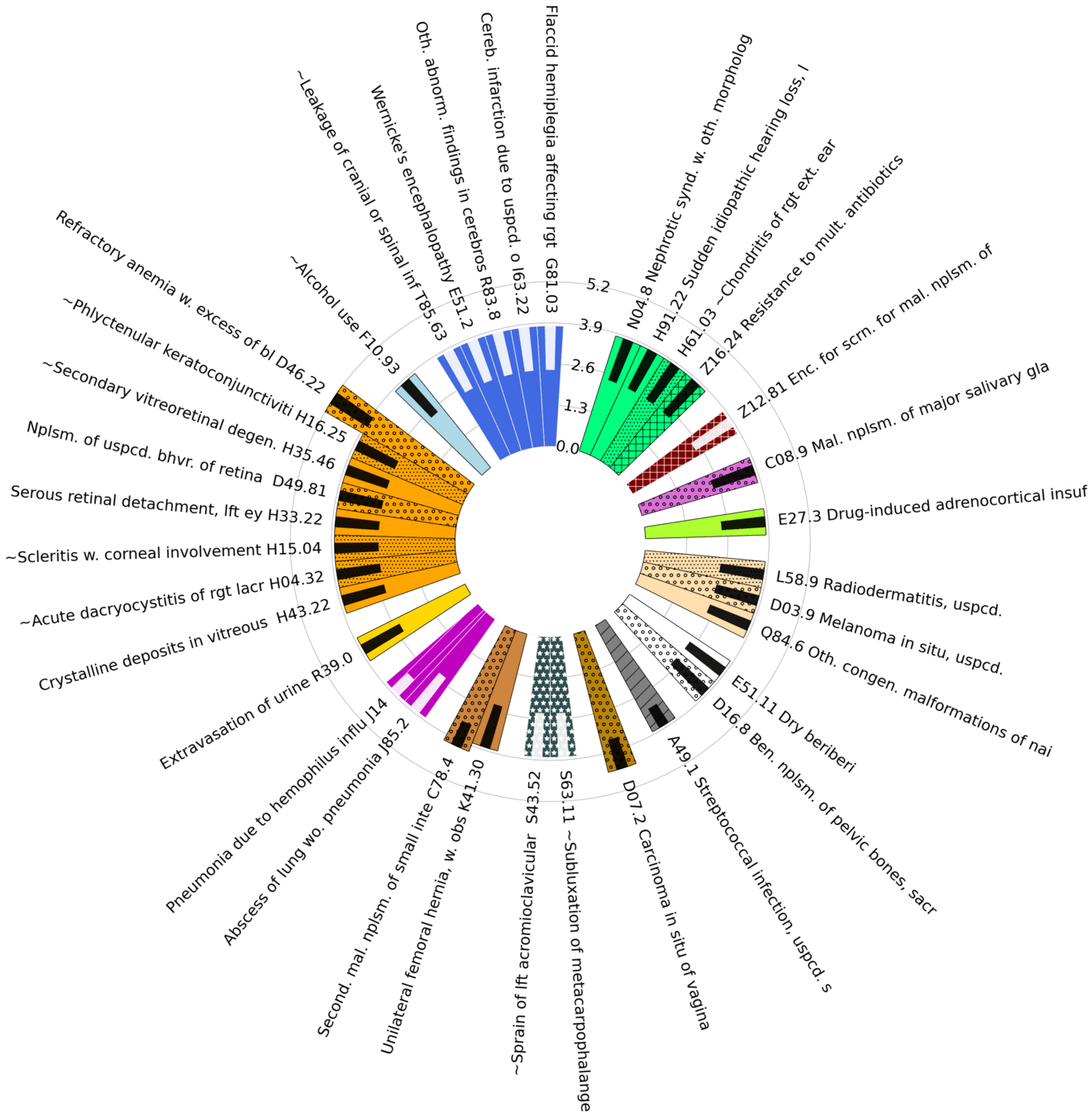

Subproblem 2.1
Diagnoses with Lowest statistically significant Absolute Log Odds Ratios by organ group

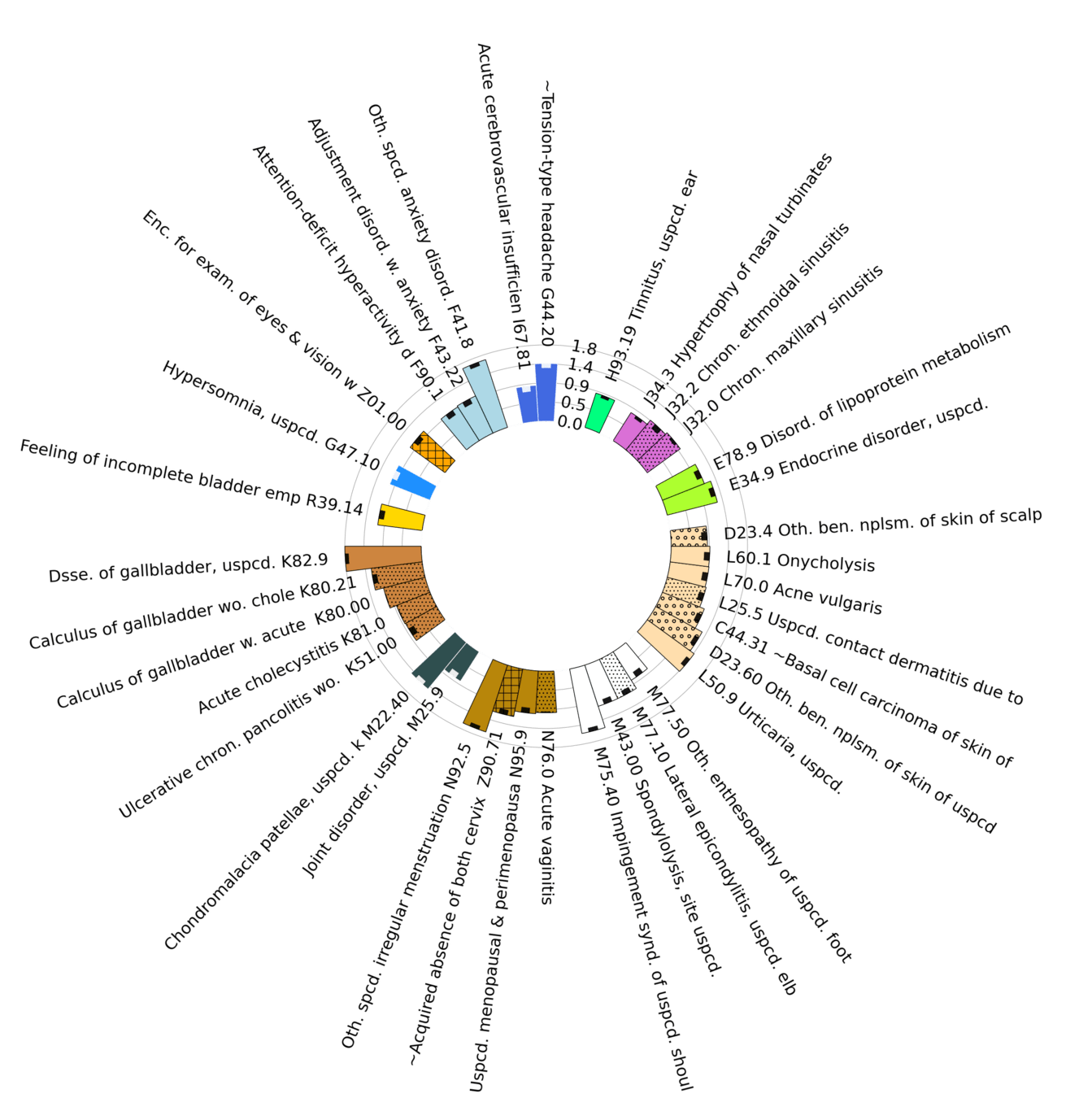
Questions:
- Is current A.P to Diabetes Mellitus progression window (2 weeks to 2 years following screening) useful for the stated purpose? Should it be shorter or longer?
- There are no ICD10 diagnostic codes that explicitly records Type 3c Diabetes Mellitus. Is current approximation of the target (Diabetes Mellitus due to underlying conditions, E08 and E13) satisfactory, given that every patient in cohort is diagnosed with A.P. and is not diagnosed with any type of Diabetes Mellitus prior to A.P. diagnosis?
- Are any of the top-risk codes presented in the slides above solid proxies for Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis? If so, should such codes be included into the prediction target, or filtered out from the cohort?
ZPAN
Subproblem 2.2
Progression from A.P. to Any Diabetes Mellitus
Subproblem 2.2 - Progression from A.P. to Any Diabetes Mellitus
Inclusion Criteria:
Patients of any age with any K85 (Acute Pancreatitis) code recorded, with >= 1 year of records leading to the first K85 diagnosis available
Exclusion Criteria:
Patients with any Diabetes Mellitus prior to the first K85 diagnosis are excluded.
Prediction Target: Any Diabetes Mellitus (E08-E13)
Time of Prediction: Date of the first K85 diagnosis
Observation window: 1 to 2 years leading to the first K85 diagnosis
Prediction Objective: Predict if any Target diagnosis will be recorded within 2 weeks to 2 years following the first K85 diagnosis
Cohort Size:
Case: 15.6k, Control: 99.6k
Males: 48,740 (42.3%), Females: 66,514 (57.7%)
Mean age at the time of prediction: 51 years 0 months
Patients with Other diseases of pancreas (K86) at the time of first K85 diagnosis:
Case: 3,012 (19.3%), Control: 13,469 (13.5%)
Subproblem 2.2 - Progression from A.P. to Any Diabetes Mellitus
Subproblem 2.2 - Progression from A.P. to Any Diabetes Mellitus
General Performance
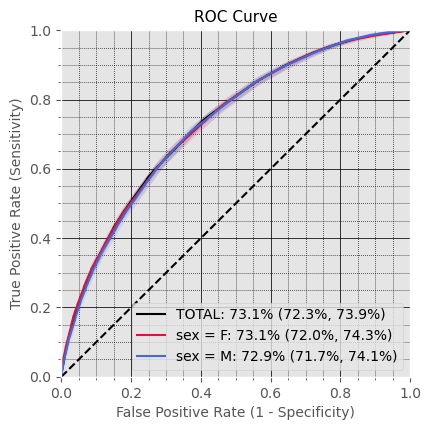
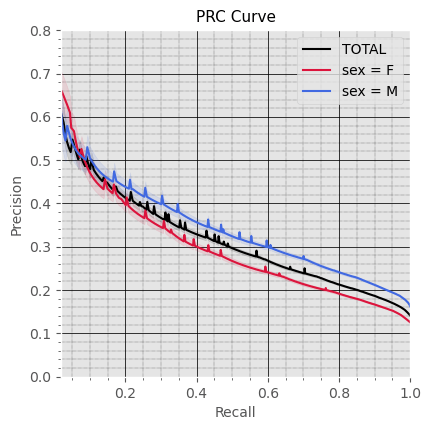
Subproblem 2.2 - Progression from A.P. to Any Diabetes Mellitus
Most influential Diagnostic Codes by mean absolute SHAP value across all True Positive patients
Male Subset
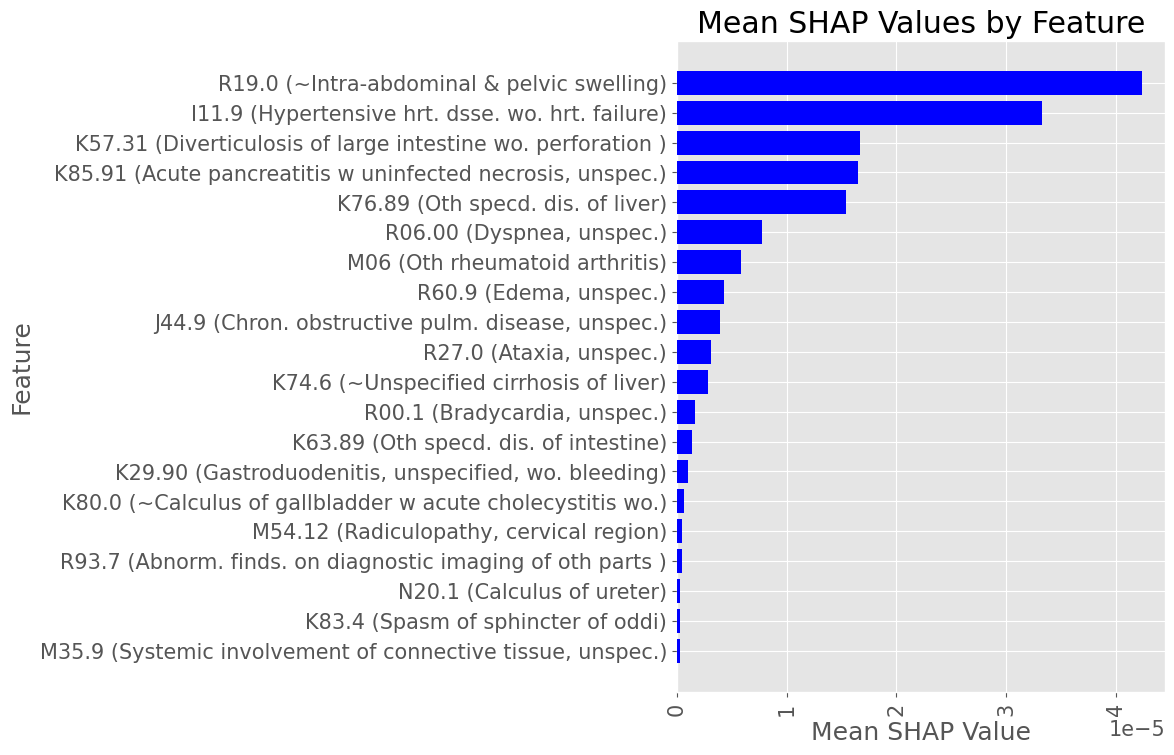
Subproblem 2.2 - Progression from A.P. to Any Diabetes Mellitus
Most influential Diagnostic Codes by mean absolute SHAP value across all True Positive patients
Female Subset
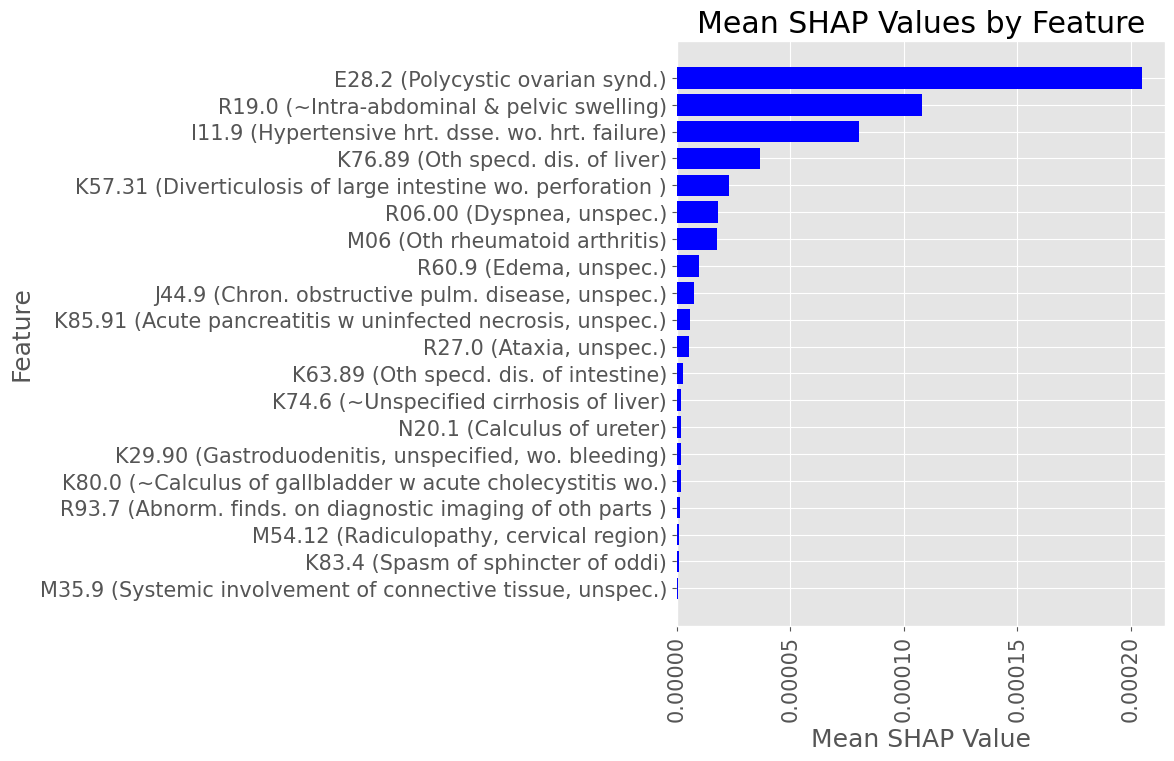
Subproblem 2.2 - Progression from A.P. to Any Diabetes Mellitus
Examples of most influential codes for True Positive patients
Male Subset
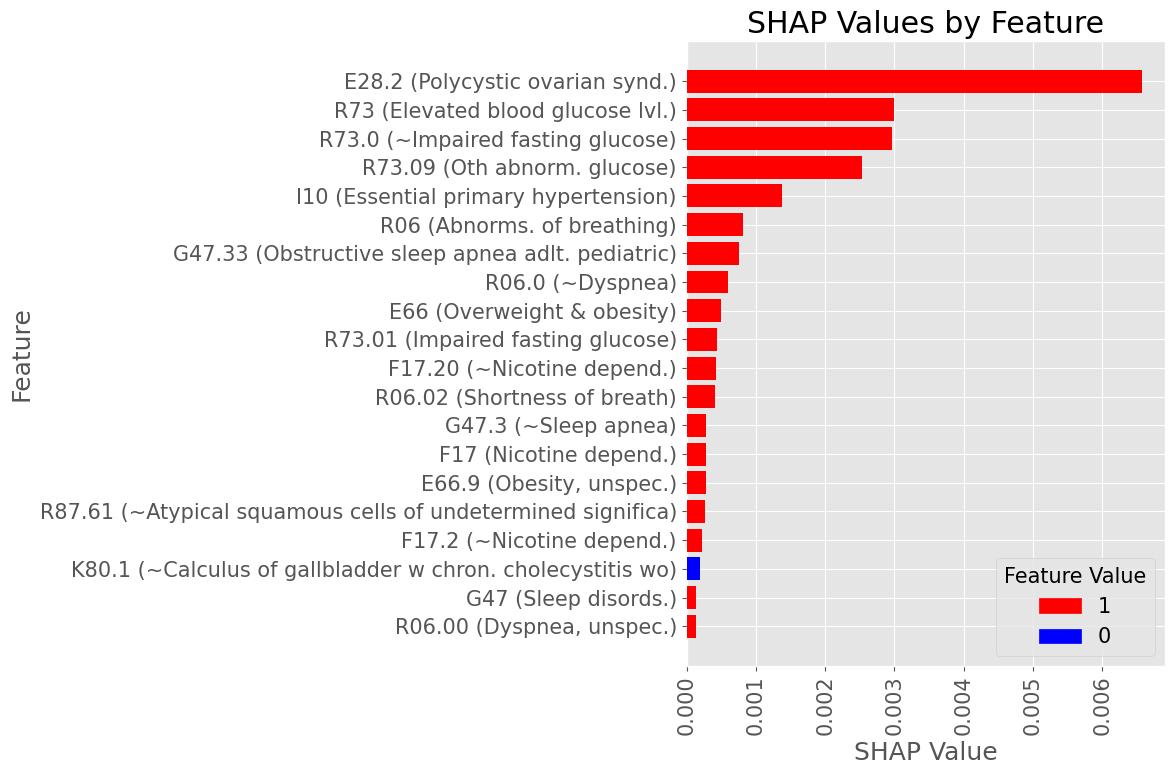
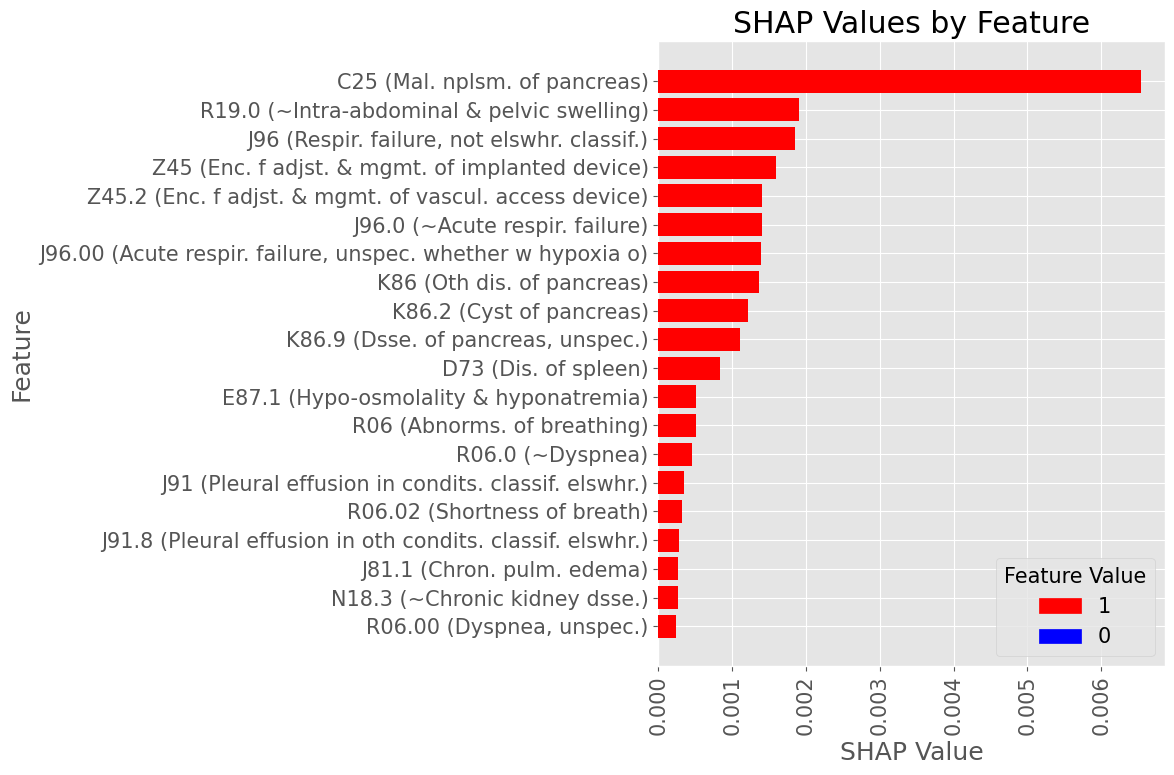
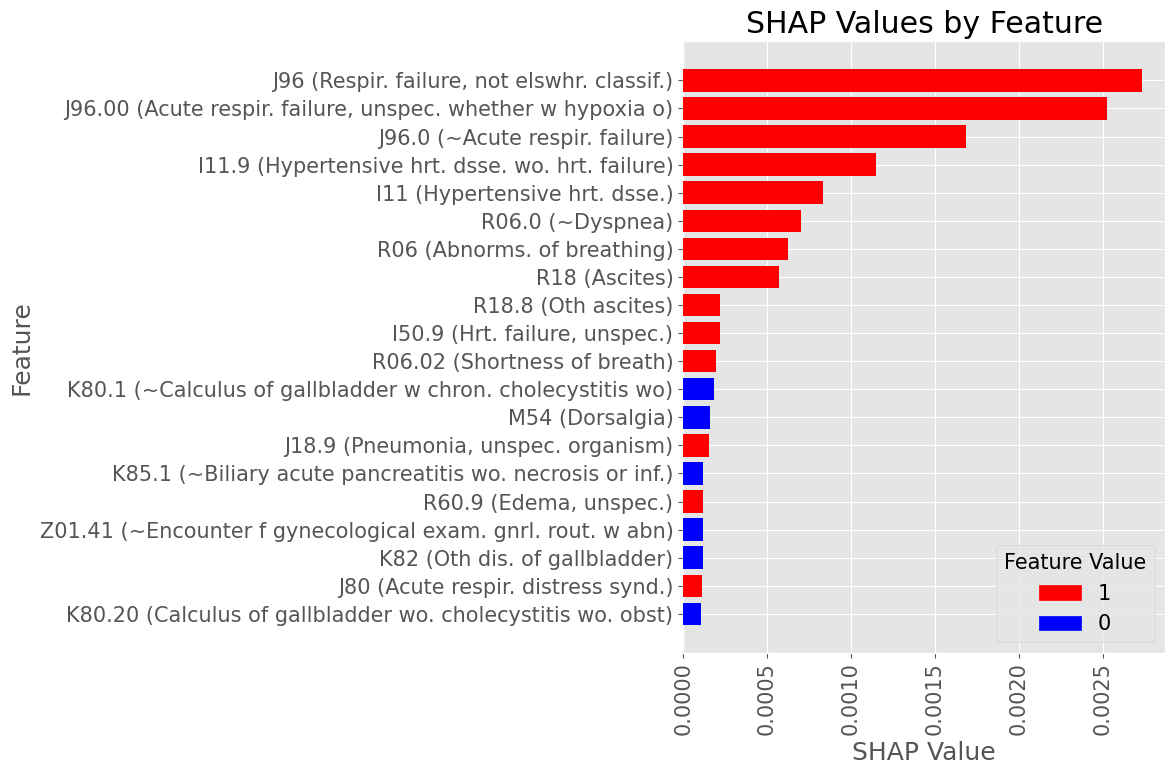
Subproblem 2.2 - Progression from A.P. to Any Diabetes Mellitus
Examples of most influential codes for True Positive patients
Female Subset



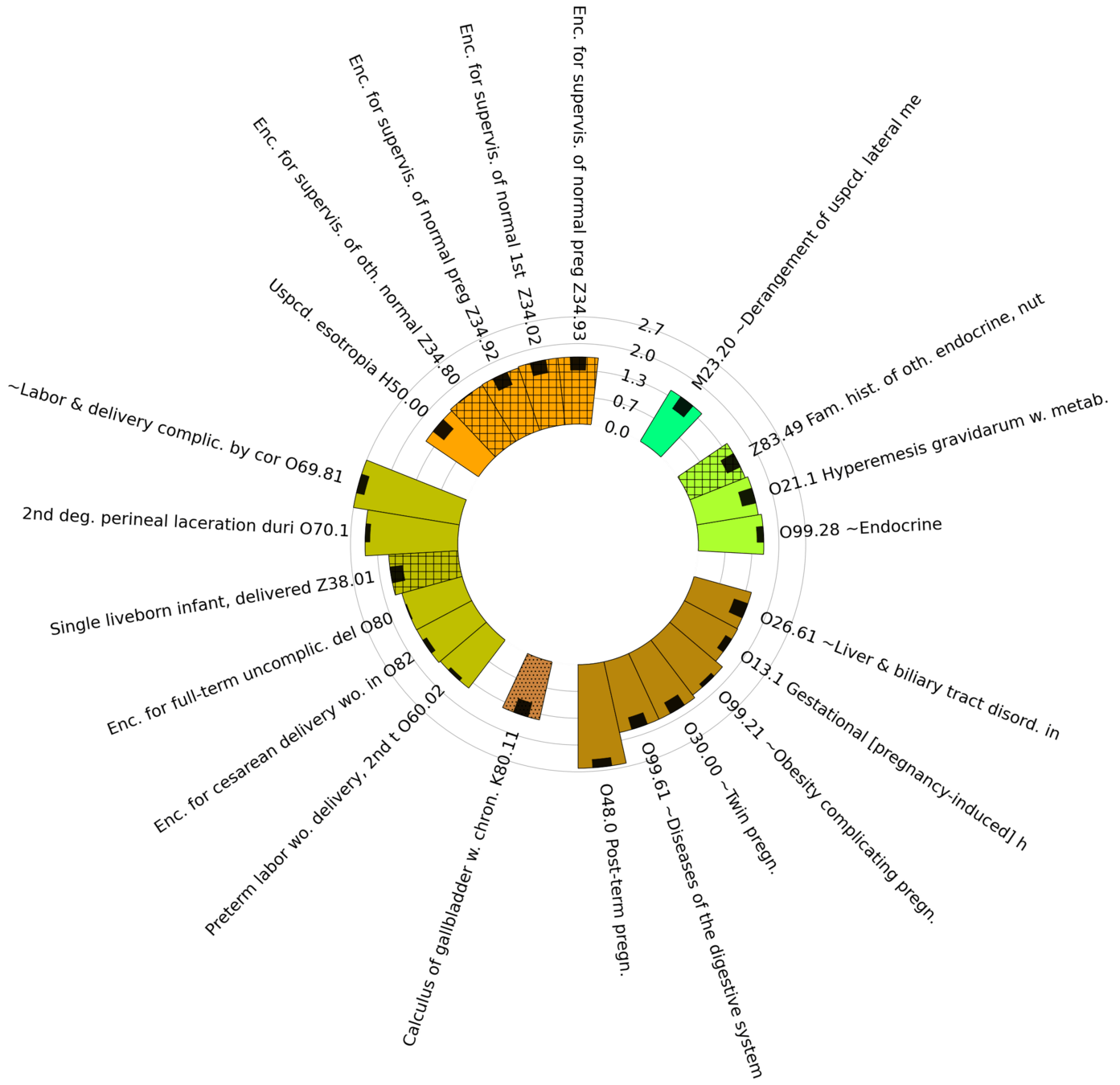
Subproblem 2.2
Diagnoses with Highest statistically significant Log Odds Ratios by organ group


Subproblem 2.2
Diagnoses with Lowest statistically significant Absolute Log Odds Ratios by organ group

Questions:
- Is current A.P to Diabetes Mellitus progression window (2 weeks to 2 years following screening) useful for the stated purpose? Should it be shorter or longer?
- Are any of the top-risk codes presented in the slides above solid proxies for Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis? If so, should such codes be included into the prediction target, or filtered out from the cohort?
ZPAN
Subproblem 3
Prediction of ICU admission following A.P. diagnosis
Subproblem 3 - Prediction of ICU admission following A.P.
Problem: There are no codes that directly mark the ICU admission in Merative MarketScan database
Closest matches, found in the inpatient admission services data are:
Place of Service (STDPLAC) -
20 Urgent Care Facility
23 Emergency Room - Hospital
27 Inpatient Long-Term Care (NEC)
41 Ambulance (land)
42 Ambulance (air or water)
Service Sub-category Code (SVCSCAT) -
10120 Facility IP Non Acute ER
10420 Facility IP Surgical ER
10520 Facility IP Medical ER
20120 Physician Specialty IP ER
21120 Physician Specialty OP ER
21220 Physician Non-Specialty OP ER
22320 Professional OP ER
Procedure Group (PROCGRP) -
111 Emergency department visits
114 ER visits, other
Provider Type (STDPROV) -
1 Acute Care Hospital
5 Ambulatory Surgery Centers
6 Urgent Care Facility
265 Critical Care Medicine
270 Endocrinology & Metabolism
275 Gastroenterology
565 Surgical Critical Care
Subproblem 3 - Prediction of ICU admission following A.P.
Problem: There are no codes that directly mark the ICU admission in Merative MarketScan database
Closest matches, found in the Procedural codes catalog are:
99291: CRITICAL CARE, EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT OF THE CRITICALLY ILL OR CRITICALLY INJURED PATIENT;
G0390: TRAUMA RESPONSE TEAM ASSOCIATED WITH HOSPITAL CRITICAL CARE SERVICE
G0508: TELEHEALTH CONSULTATION, CRITICAL CARE, INITIAL , PHYSICIANS TYPICALLY SPEND 60 MINUTES COMMUNICATING WITH THE PATIENT AND PROVIDERS VIA TELEHEALTH
G0509: TELEHEALTH CONSULTATION, CRITICAL CARE, SUBSEQUENT, PHYSICIANS TYPICALLY SPEND 50 MINUTES COMMUNICATING WITH THE PATIENT AND PROVIDERS VIA TELEHEALTH
G9657: TRANSFER OF CARE DURING AN ANESTHETIC OR TO THE INTENSIVE CARE UNIT
Subproblem 3 - Prediction of ICU admission following A.P.
Questions:
- What of the presented codes count as an indicator of ICU admission?
- Any other commonly used indicators of ICU admissions we should include in the prediction target?
- What is the useful prediction window for ICU admission following A.P. Dx? Is 2 weeks after A.P. too early? Is 2 years after A.P. too late?
- Within the useful prediction window, do any ICU admissions count, or such an admission should be related to A.P. complications?
ZPAN
By Dmytro Onishchenko
ZPAN
- 386
