Testing Techniques

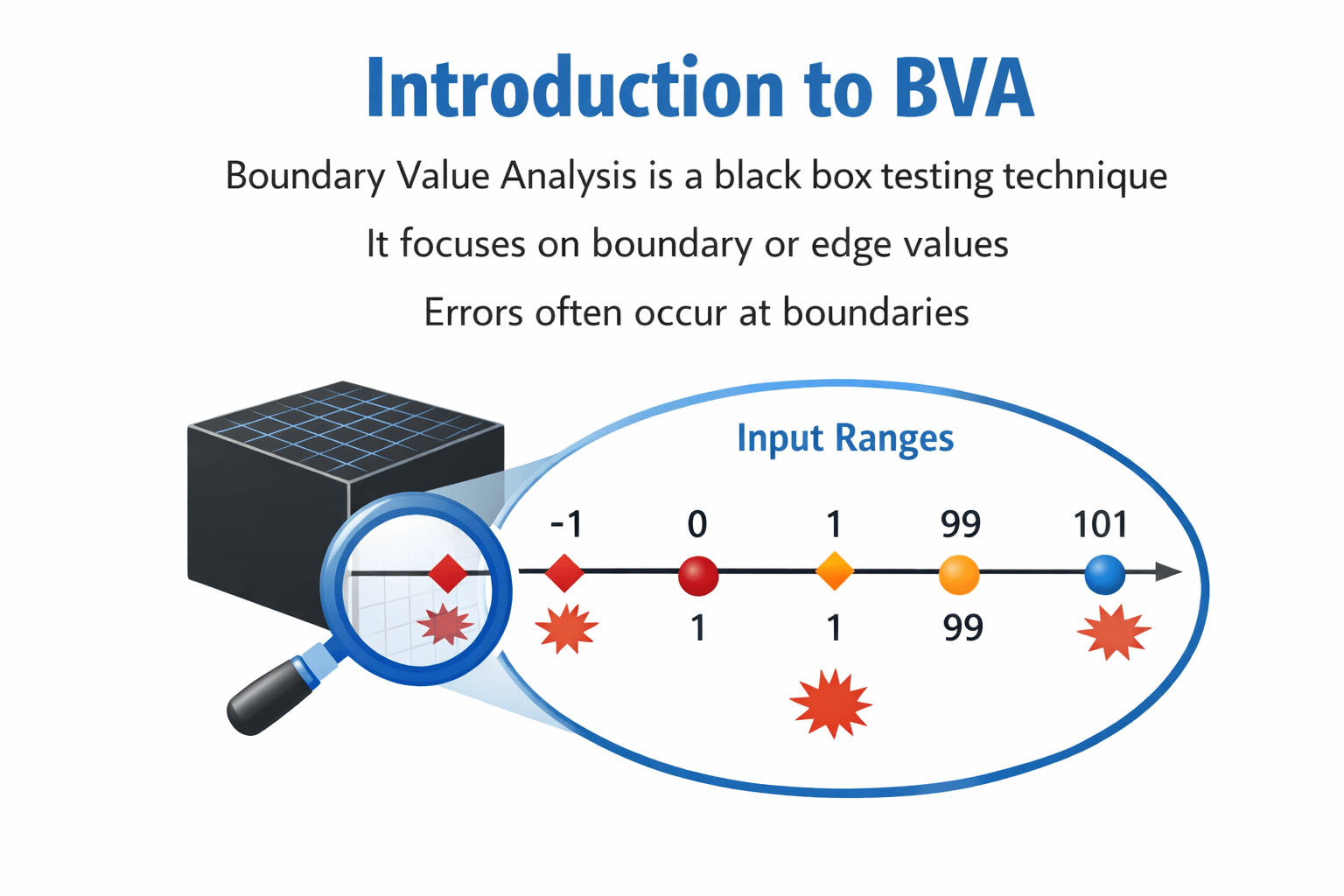
Boundary Value Analysis


Use this slide if there is no Heading
Note - Create Content inside Red Layout
[Delete Red Outline After creating slide]

Learning Outcome(Slide2)
3
Design test cases using BVA
2
Identify boundary values
1
Understand Boundary Value Analysis

Topic Name-Recall(Slide3)

Hook/Story/Analogy(Slide 4)

Transition from Analogy to Technical Concept(Slide 5)

Valid and Invalid Equivalence Classes

Valid and Invalid Equivalence Classes
Produces expected output
System should accept these values
Contains correct and acceptable input values
System should reject these values
Error message should be displayed
Contains incorrect or unacceptable input values






Invalid Equivalence Class
Valid Equivalence Class

Steps to Apply BVA
Identify boundary values
Create test cases using boundary values
Identify input range



Advantages and Limitations of BVA
Advantages
- Simple and effective
- Finds boundary-related defects
- High defect detection rate



Limitations
- Usually combined with ECP
- Not suitable for complex logic
- Only focuses on boundaries


Difference Between ECP and BVA
ECP tests groups of data
Both are black box techniques
BVA tests edges of data




Summary
3
Best used with ECP for effective testing
2
Focuses on boundary values
1
BVA is an important black box testing technique

Quiz
Which of the following is a boundary value for the range 10–50?
A. 25
B. 10
C. 30
D. 40


Quiz-Answer
Which of the following is a boundary value for the range 10–50?
A. 25
B. 10
C. 30
D. 40
